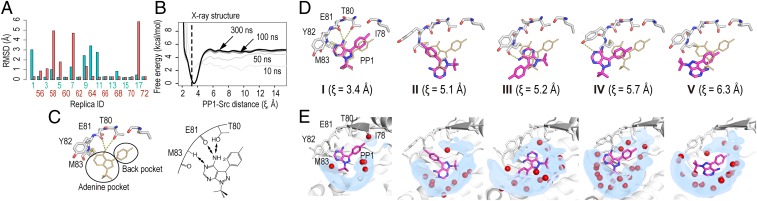
Fig. 2.
Structures and hydration of bound states. (A) Minimum values of heavy atoms rmsd of the ligand PP1 from the X-ray structure (1QCF) for selected replicas (replica indexes of 1 to 18 and 55 to 72). (B) Free-energy profiles at 310 K along the PP1-Src distance (ξ). The PP1-Src distance (ξ) in the X-ray structure (1QCF, ξ = 3.25 Å) is shown as a dotted line. (C) The X-ray structure with 2 dominant pockets: the adenine pocket for hydrogen bonding with the hinge region and the back pocket for hydrophobic interaction. The hydrogen bonds between PP1 and hinge residues are shown by the yellow dotted line. (D) The bound (I) and semibound (II–V) poses obtained from the simulation. PP1 in the X-ray structure is shown in gold for comparison. The hydrogen bonds between PP1 and hinge residues are preserved in pose I, but not in the semibound poses. (E) Volume map representation of water distribution (isosurface at 20% occupancy) around the binding pocket. Red spheres in the bound (I) and the semibound (II–V) poses, respectively, represent water molecules in the X-ray structure and from the simulation. The poses I, II, III, IV, and V, respectively, correspond to Bzz, Bpp, Bpz, Bzz*, and Bzp in Figs. 3 and 4.