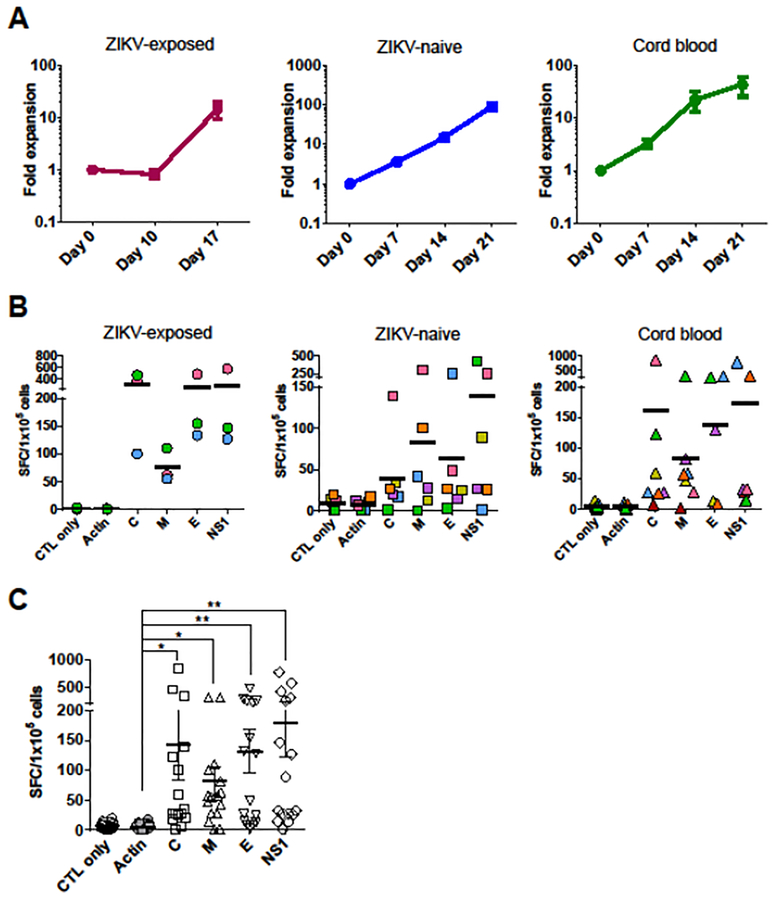
Figure 1. ZIKV-specific T-cells can be expanded from ZIKV-exposed, ZIKV-naïve adult donors and umbilical cord blood.
(A) Fold expansion of ZIKV-specific T-cell products generated from ZIKV-exposed donors (n = 3), ZIKV-naïve adult donors (n = 6), and cord blood (n = 7) based on the fold increase in the total cell numbers (mean ± SEM). (B) Specificity of ZIKV-specific T-cells from ZIKV-exposed donors (n = 3), ZIKV-naïve adult donors (n = 6), and cord blood (n= 7) with response to ZIKV antigens stimulation by IFN-γ ELISpot assay. Stimulation with actin was used as a negative control. Results are presented as SFC/1 × 105 cells. Bars denote the means. The same figure/color plot is from the same individual donor. (C) Specificity of ZIKV-specific T-cells from all cohort donors (n = 16) with response to ZIKV antigens (mean ± SEM; *P = 0.0002, **P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test).