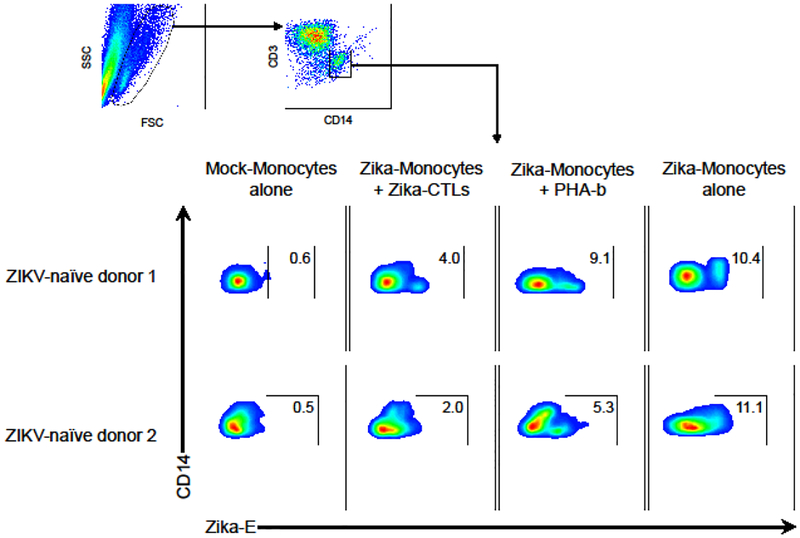
Figure 4. ZIKV-specific T-cell products kill ZIKV-infected targets.
CD14-selected monocytes were infected with ZIKV (strain PRVABC59) and used as target cells in the coculture cytotoxicity assay. ZIKV-specific CTLs (CD3+) were cocultured with autologous ZIKV-infected CD14+ monocytes at an effector/target ratio of 2:1 for 24 hours. Autologous PHA-blasts were used as a negative control. CD3− and CD14+ fraction was gated and the presence of ZIKV-infected targets (Zika-E+) were assessed by flow cytometry. Uninfected monocytes (mock-monocytes alone) were used as negative control of accessing infected targets and infected monocytes (Zika-monocytes alone) were used as positive control.