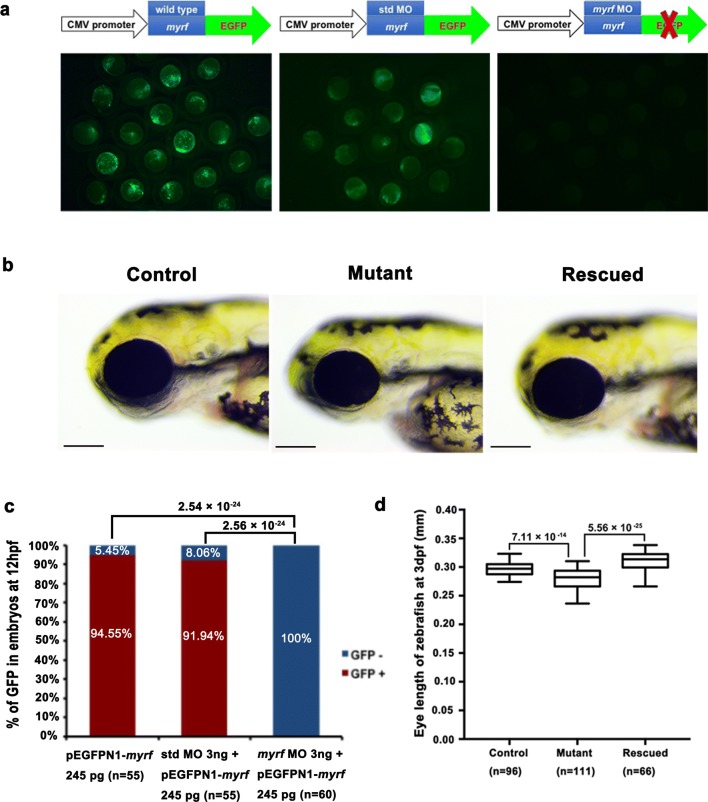
Fig. 4.
Phenotype of myrf knockdown zebrafish. a The efficiency of myrf MO knockdown of the myrf gene. Strong GFP signals were present in the left and middle images, which represent injection with myrf-pEGFPN1 plasmid alone and coinjected of myrf-pEGFPN1 plasmid with std MO, respectively. No GFP signal was detected in the embryos coinjected with myrf-pEGFPN1 plasmid and myrf MO, as shown in the right image. b Embryos with myrf knockdown showed a phenotype of small eye size (middle image) compared to the std MO-injected embryos (left image). This phenotype could be rescued by coinjection of myrf mRNA (right image). Control is larvae injected with 3 ng of std MO at 72 hpf. Mutant is larvae injected 3 ng of myrf MO at 72 hpf. Rescue is larvae coinjected with 3 ng of myrf mRNA and 106 pg of myrf MO at 72 hpf. c Proportions of embryos with GFP+ or GFP− treated with 245 pg pEGFPN1-myrf, co-injection of 3 ng std MO with 245 pg of pEGFPN1-myrf and coinjection of 3 ng myrf MO with 245 pg of pEGFPN1-myrf. The p values by the Chi-squared test are shown above. d Box plot of the median and deviations of eye size in three groups. The p values by one-way ANOVA are shown above