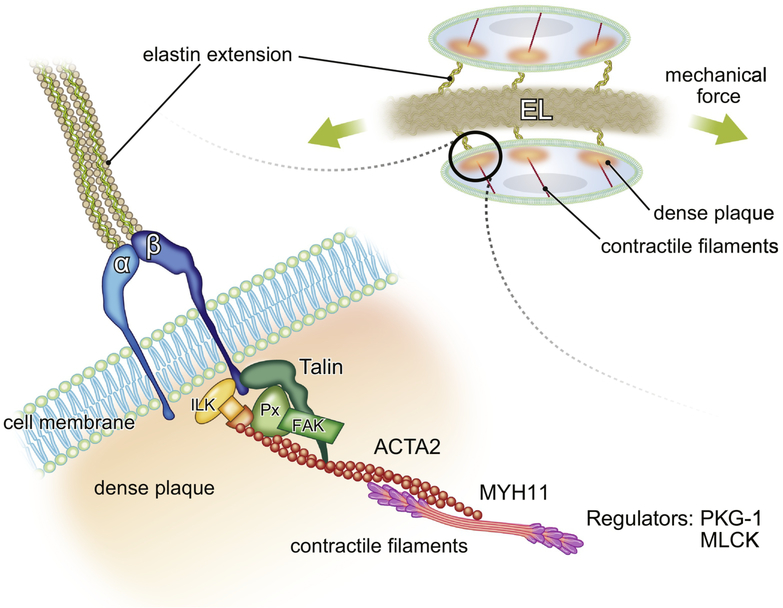
Figure 3. Schematic presentation of the elastin-contractile unit in SMCs.
Elastic fibers bind to α- and β- heteromeric integrins through elastin extensions and form dense plaques (orange), where focal adhesion proteins such as Talin, paxillin (Px), focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and integrin linked kinase (ILK) bind and regulate contractile filaments (red, major isoform is ACTA2) as well as activate various downstream signaling. Cellular tension is generated by the contraction of actin and myosin (pink, major isoform is MYH11). The regulators of muscle contraction such as PKG-1 and MLCK also play a crucial role in response to mechanical stimuli. The defects in elastin-contractile units result in the formation of thoracic aortic aneurysms. EL: elastic lamina.