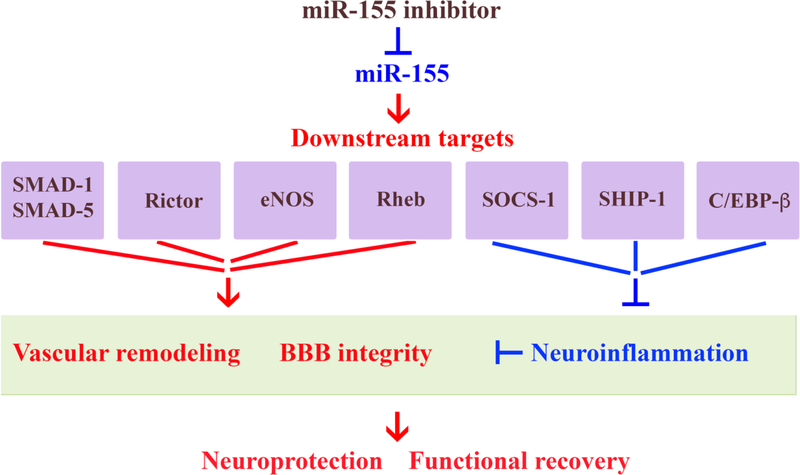
Figure 2: Possible molecular mechanisms mediating functional recovery supported by in vivo miR-155 inhibition after stroke.
miR-155 inhibition results in the increased expression of miR-155 target proteins SMAD-1 and SMAD5 (components of BMP signaling pathway), Rictor (mTOR pathway), eNOS (NO pathway), Rheb (activates Akt/ZO-1 pathway), which support microvascular function and strengthen the BBB integrity. Upregulation of other miR-155 targets, such as SOCS-1 and SHIP-1 (which suppress JAK/STAT-mediated cytokine signaling), and C/EBP (which activates anti-inflammatory IL-10), regulate post-stroke neuroinflammation and thus, support vascular integrity and neuronal survival. As a result, miR-155 inhibitor-induced support of BBB integrity leads to the reduction of brain edema, restoration blood flow in the peri-infarct area of stroke, and prevents delayed neuronal death in the peri-infarct area. This results in the reduced brain infarct, neuroprotection and improved functional recovery. Red font/arrow indicate upregulation/activation; blue - downregulation/inhibition.