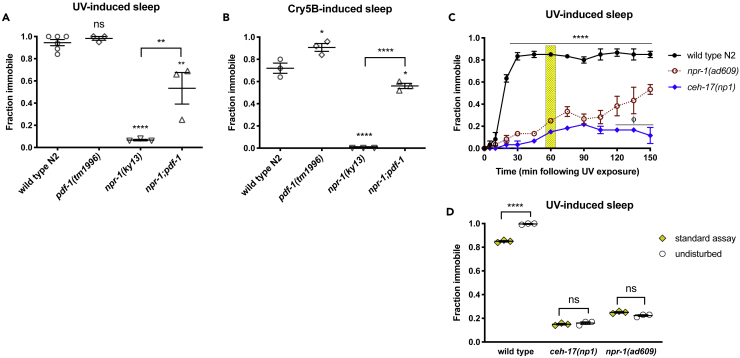
Figure 3.
The SIS Defect in npr-1(lf) Is Influenced by PDF-1 Secretion but Is Not Attributable to Heightened Mechanosensation
(A and B) Animals were assayed for SIS in response to UV light (A) or Cry5B toxin (B) as described in methods. Each data point represents the fraction of immobile animals in one trial of 25 young adult hermaphrodites. Mean and SEM of multiple independent trials are indicated. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ns, not significant versus Wild-type (or versus genotype indicated by connecting bars), one-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test.
(C) Time course of locomotor quiescence following UV light exposure. In this standard assay, plates are gently moved into the stereomicroscope field of view 45 s before each time point. npr-1(lf) animals are defective in locomotor quiescence following UV exposure, similar to ALA-defective ceh-17(lf) but ultimately engage in partially penetrant SIS. Mean and SEM of three trials of at least 20 animals per trial are shown. ****p < 0.0001 wild-type versus npr-1(ad609), φ p < 0.01 npr-1(ad609) versus ceh-17(np1), two-way RM ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test.
(D) The SIS defect of npr-1(lf) does not appear to be attributable to heightened touch sensitivity. The 60 min time point from the time course in (C) (yellow shading) is compared with that of single-time point assay in which plates are left completely undisturbed 60 min before examination. Wild-type, but not npr-1(lf), animals show increased locomotor quiescence in response to reduced mechanosensory input. Each data point represents the fraction of immobile animals in one trial of at least 20 young adult hermaphrodites. Mean and SEM of multiple independent trials are indicated. ****p < 0.0001, ns, not significant, multiple Student's t tests with Holm-Sidak correction.