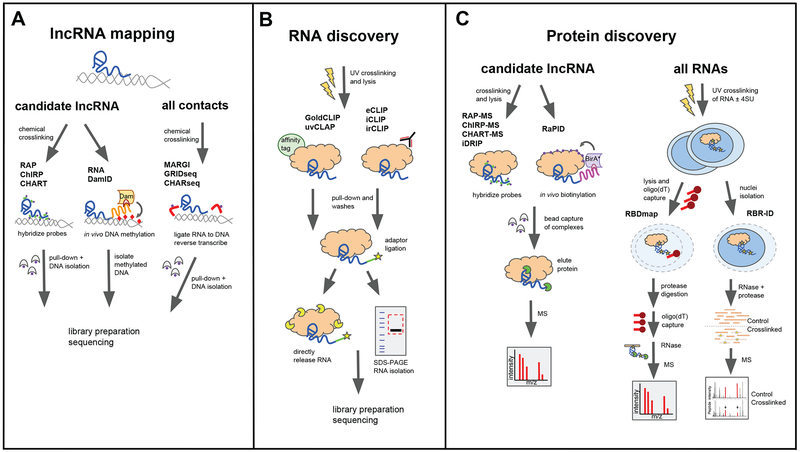
Figure 2. Methods for mapping the lncRNA interactome.
(A) Outline of methods to study lncRNA localization on chromatin. RAP, ChIRP, and CHART (left) use chemical crosslinking and biotinylated probes to capture a candidate lncRNA crosslinked to chromatin and identify its genomic targets by sequencing the associated DNA. In RNA DamID (middle) cells express a lncRNA of interest fused to MS2 stem-loop sequences and a E. coli adenine methyltransferase (Dam) fused to the MS2 coat protein. This results in methylation at lncRNA-bound genomic sites in vivo. Methylated DNA is then isolated with a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme and sequenced. MARGI, GRIDseq, and CHARseq (right) use a biotinylated oligonucleotide bridge to ligate RNA to DNA in close proximity, followed by affinity purification of ligated complexes, library preparation, and sequencing.
(B) Schematic of methods used to identify RNA interactors of a given RBP. GoldCLIP and uvCLAP use affinity handles to purify crosslinked protein–RNA complexes, followed by adaptor ligation and direct elution of bound RNAs for sequencing. eCLIP, iCLIP, and irCLIP use protein-specific antibodies, SDS-PAGE, membrane transfer, and membrane excision to isolate RNAs for sequencing.
(C) Outline of methods to identify lncRNA-protein interactions. Left: methods to detect protein interactors of a candidate lncRNA. RAP-MS, ChIRP-MS, and CHART-MS chemically crosslink RNA to protein, use biotinylated probes to capture target lncRNA-protein complexes, and digest with RNase to release bound proteins for mass spectrometry; RaPID targets the BirA* biotin ligase to a stem-loop modified RNA to biotinylate protein interactors in live cells. Right: methods to identify new RBPs that bind to RNA in cells. RBDmap (left) and RBR-ID (right) use UV to crosslink RNA to protein in live cells in the presence of absence of 4SU. RBDmap lyses cells and employs two rounds of oligo(dT) capture to enrich for polyadenylated transcripts (left). RBR-ID isolates cell nuclei to identify all nuclear RNA-binding proteins. Both methods include RNAse digestion and protease digestion steps to generate short crosslinked peptides that can be analyzed by MS (bottom).