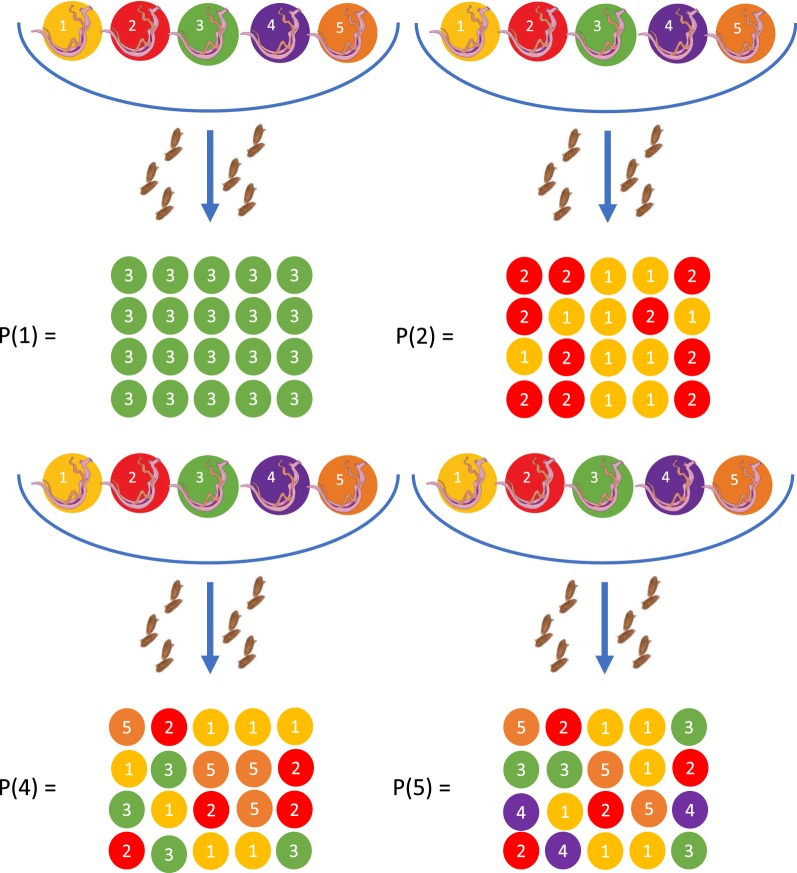
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the unique items distribution. If a host is infected with five female worms/parental genotypes N = 5, and m = 20 miracidia/offspring are sampled, genotyped and subjected to sibship analysis (assuming 100% accuracy of the sibship reconstruction) then P(1), P(2), P(4) and P(5) are the probabilities of identifying exactly n = 1, n = 2, n = 4 and n = 5 unique parental genotypes. The expected value of n, E(n), depends on the values of N and m following the expression given in Equation 3. The bias in E(n) as an (under)estimate of N (expressed as a percentage) is [E(n) − N]/N. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art according to a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License guidelines 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)