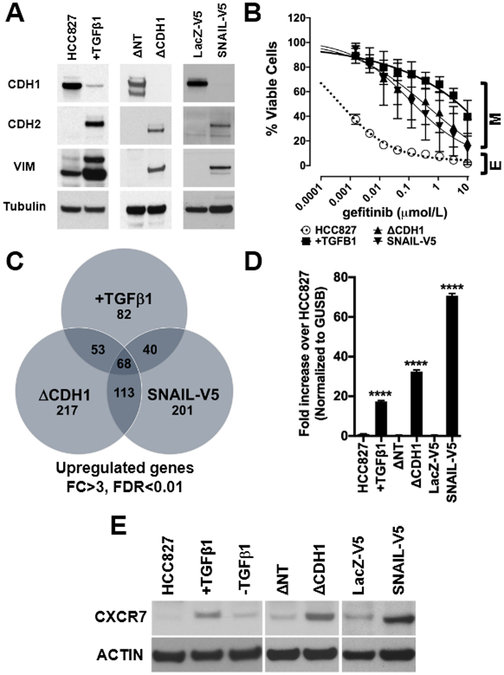
Figure 1. Induction of a mesenchymal phenotype in HCC827 cells promotes overexpression of CXCR7.
A. Chronic exposure to TGFβ1 (+TGFβ1), shRNA-mediated E-cadherin depletion (ΔCDH1), and ectopic expression of SNAIL-V5, induce canonical EMT markers (CDH1: E-cadherin, CDH2: N-cadherin, VIM: vimentin) in EGFR mutant HCC827 cells. Non-target shRNA (ΔNT) and LacZ-V5 are controls. B. The induction of a mesenchymal phenotype (M) renders in HCC827 epithelial cells (E) resistant to gefitinib. (n=5, Error bars: S.D.) C. Gene expression profiling identifies commonly upregulated genes in cells with EMT (fold change >3, FDR<0.01) and identifies CXCR7 as one of 68 mutually overexpressed genes. D. Taqman qRT-PCR using CXCR7 probe in HCC827 with EMT (+TGFβ, ΔCDH1, and SNAIL-V5). (n=3, Error bars: S.D.) (****p≤0.0001). E. Immunoblot showing CXCR7 expression in EGFR mutant NSCLC cells with mesenchymal phenotype (ΔCDH1 and SNAIL-V5). ACTIN as loading control. The image is representative of three independent experiments.