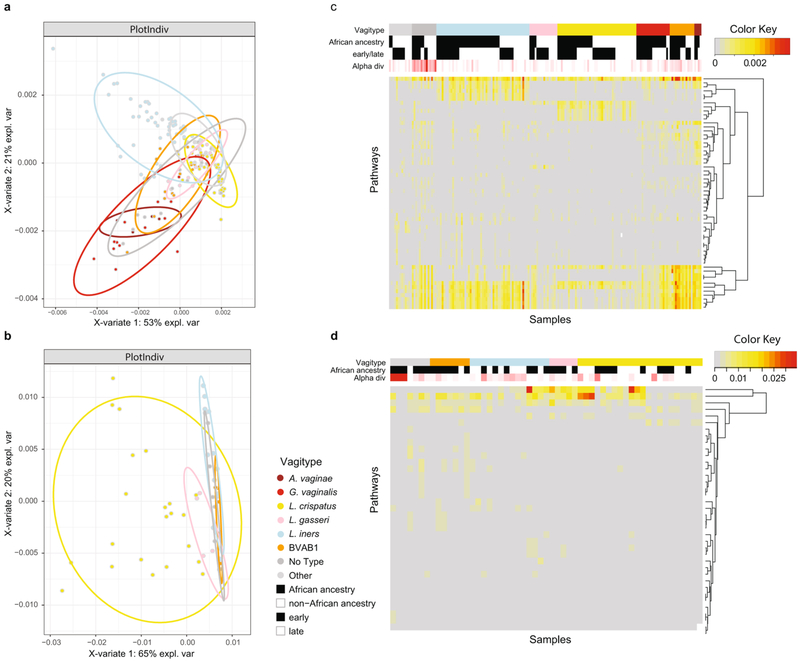
Extended Data Fig. 7 ∣. Functional metabolic potential and transcriptional activity in vaginal microbiomes cluster according to vagitype.
a, Sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) of pathways derived from metagenomic sequence analysis of all 373 samples (147 samples from the 41 women of non-African ancestry, and 226 samples from the 49 women of African ancestry) from the 90 women in this study. Samples are color-coded according to vagitype (see legend). b, Sparse PLS-DA of pathways derived from metatranscriptomic sequence analysis of 1 sample from each pregnancy taken in the second or early third trimester (20 samples from the women of non-African ancestry and 28 from the women of African ancestry). c, Heat map of pathways from metagenomic analysis of samples as for a. Samples are sorted according to major vagitype (see legend). Samples from women of African ancestry (African) and from prior to 26 weeks’ gestation (early) are indicated. Alpha diversity is shown. d, Heat map of pathways from metatranscriptomic analysis of samples as for b. Samples are sorted as in c. Abundance and alpha diversity value scales are indicated. Sparse PLS-DA is a technique for fitting classification models that simultaneously selects features (via an L1 norm penalty term) that best describe group separation. The resulting model is sparse so that only a small subset of bacteria is included; the discriminant functions allow for visualization of the classification rule.