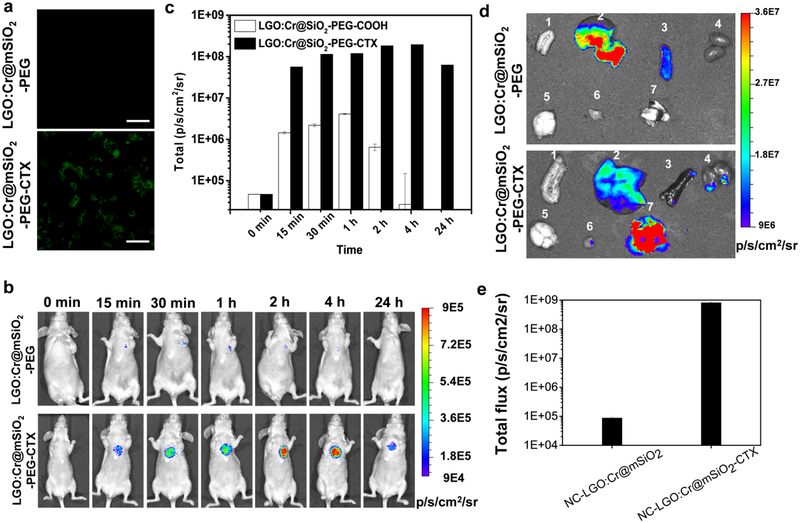
Figure 6.
Tumor targeting of NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2-CTX. a) In vitro microscopic analysis, conducted with H1299 cells. NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2-CTX can be efficiently internalized by H1299 cells. As a comparison, NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2 showed minimal cell uptake. Scale bars: 100 μm. b) In vivo imaging, based on XEOL signals and assessed in H1299 lung tumor models. NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2 and NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2-CTX nanoparticles (0.4 mg per animal) were intravenously injected to the animals. For imaging, X-ray (0.02 Gy) was applied to the lung areas, followed by immediate BLI. Strong luminescent signals in the lung were found in the NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2-CTX group but not the NC-LGO:Cr@mSiO2 group. c) XEOL intensity changes, based on BLI imaging results from b). d) Ex vivo images with dissected tissues from b). 1. Intestine; 2. liver; 3. spleen; 4. kidneys; 5. brain; 6. muscle; 7. lung. e) Luminescent intensity changes, based on BLI imaging results from d).