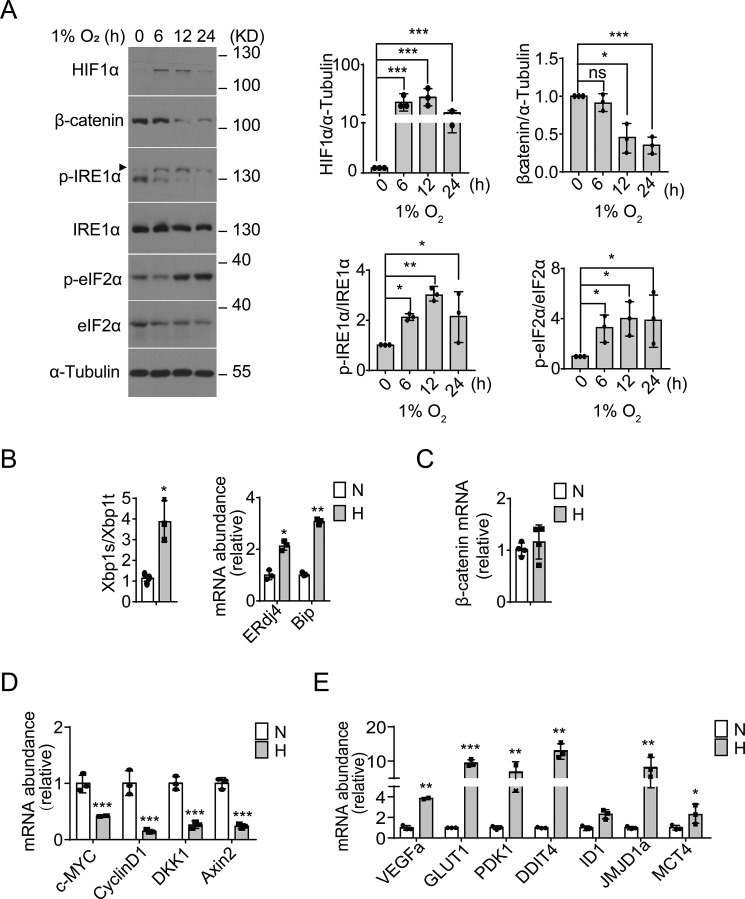
Figure 1.
Hypoxic ER stress accompanies down-regulation of β-catenin signaling in RKO cells. A, RKO cells were cultured under moderate hypoxia conditions (1% O2) for the indicated time intervals. Protein expression levels of HIF1α and β-catenin, as well as phosphorylation of IRE1α (p-IRE1α) and eIF2α (p-eIF2α), were analyzed by immunoblotting. Quantification of HIF1α and β-catenin levels (relative to α-tubulin) and p-IRE1α/IRE1α and p-elF2α/elF2α ratios is shown after normalization to the value at 0 h. B–D, RKO cells were cultured under hypoxia (H, 1% O2) or normoxia (N, 21% O2) for 12 h. B, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the spliced form of XBP1 (XBP1s) mRNA relative to the total amount of XBP1 (XBP1t) mRNA, and the mRNA levels of ERdj4 and Bip (relative to actin). Values were normalized to normoxic levels. C–E, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of β-catenin (C), β-catenin target genes (c-MYC, cyclin D1, DKK1, and AXIN2) (D), and hypoxia-responsive HIF1α target genes (VEGFa, GLUT1, PDK1, DDIT4, ID1, JMJD1a, and MCT4) (E). All data are shown as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test.