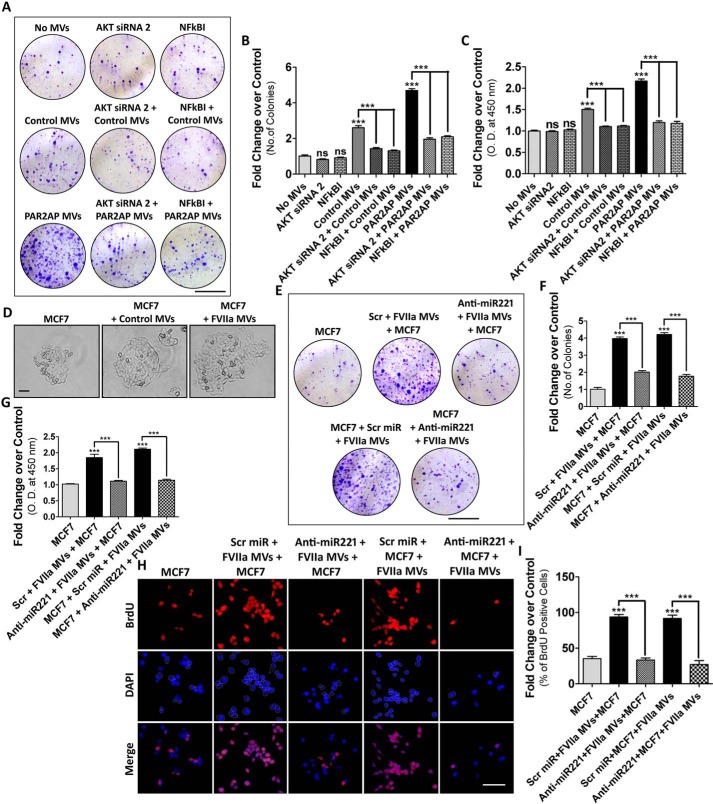
Figure 3.
MDAMB231-MV–mediated transfer of miR221 induces MCF7 cell proliferation in vitro. MCF7 cells were treated with AKT siRNA2 or NF-κBI followed by the incorporation of MDAMB231 cell-derived MV. Recipient MCF7 cell proliferation was analyzed by: A and B, colony formation assay; scale bar 10 mm; and C, BrdU incorporation assay with HRP-tagged secondary antibody, which suggests that the inhibition of AKT or NF-κB significantly reduced MDAMB231-MV–induced proliferation of MCF7. D, imaging of single cell growth of MCF7 upon fusion of MDAMB231-derived MV suggests that the MCF7 growth rate increases remarkably upon fusion with MDAMB231-MV and the maximum effect was observed when PAR2-activated cell-derived MV were incorporated. MDAMB231 cells were transfected with anti-miR221 beside Scrambled control followed by FVIIa treatment. MV were fused with MCF7 cells. Alternatively, MCF7 cells were transfected with anti-mi221 followed by the fusion of MDAMB231-MV. The recipient MCF7 cell proliferation was analyzed by E and F, colony formation assay; scale bar 10 mm; and G–I, BrdU incorporation assay; scale bar 25 μm. Introduction of anti-miR221 significantly reduced MDAMB231-MV–induced MCF7 proliferation.