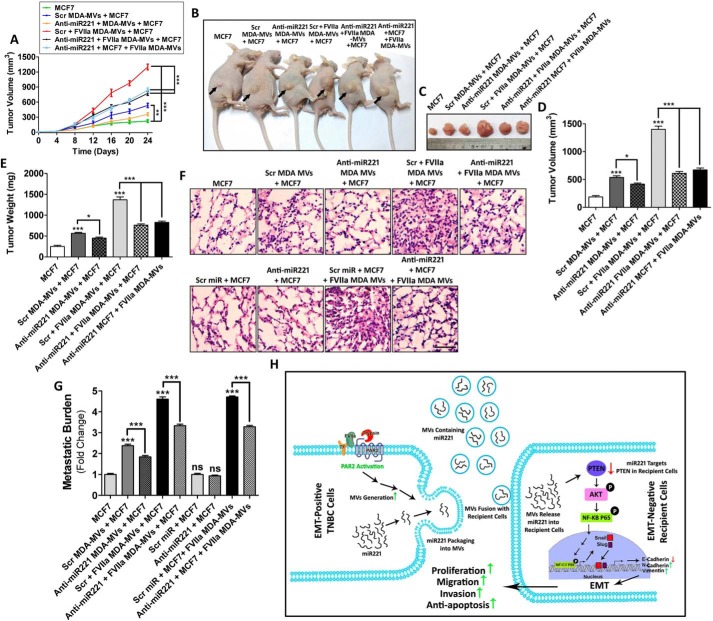
Figure 6.
miR221, transported via MDAMB231-MV, promote proliferation and metastasis of MCF7 in vivo. A, anti-miR221 was transfected into the donor MDAMB231 cells followed by the addition of FVIIa. MV were isolated and fused with MCF7 cells. Alternatively, anti-miR221 was introduced into MCF7 directly prior to the incorporation of FVIIa-treated MDAMB231-MV. Recipient MCF7 cells were introduced into the 6-week-old female BALB/c nude mice via subcutaneous injection (n = 7 in each group). Mice were sacrificed and tumor volume was measured in a day-wise manner up to 25 days. B and C, representative images of tumors at the 25th day, D and E, and after euthanization tumors were excised and tumor volume as well as weight were measured and accordingly comparative graphical analyses were performed. FVIIa-treated, MDAMB231-derived MV promoted MCF7 proliferation in vivo but the introduction of anti-miR221 reversed the effect suggesting that the process depended on miR221. To determine the metastatic potential of MDAMB231-derived MV, MV-fused MCF7 cells (1 × 106) were introduced into 6-week-old female BALB/c nude mice by tail vein injection (n = 7 in each group). After 25 days, mice were euthanized and lungs were harvested. F, a part of the lung was subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining; scale bar 50 μm, whereas G, from the other part genomic DNA, was isolated by phenol-chloroform method. The isolated genomic DNA was subjected to PCR amplification with human-specific HK2 primers as well as 18S rRNA primers by real-time PCR. Relative metastatic burden was quantified accordingly. Similar to the proliferation data, FVIIa-treated, MDAMB231-derived MV also induced miR221-dependent metastasis of MCF7. H, schematic diagram showing that MV, isolated from MDAMB231 upon PAR2 activation induces proliferation, migration, invasion, and anti-apoptosis of MCF7 cells via the transfer of miR221. The activation of PAR2 results in the generation of miR221-laden MV from the human TNBC cell line, MDAMB231. The MV readily fuse with less aggressive MCF7 cells thereby transporting MDAMB231-derived miR221 into MCF7. This leads to the down-regulation of PTEN followed by the activation of AKT and NF-κB/p65, which results in Snail and Slug up-regulation whose ultimate effect is the EMT via minimizing E-cadherin expression, whereas up-regulating N-cadherin and vimentin expression. This ultimately leads to the enhancement of proliferation, migration, and invasion of recipient MCF7 cells while also imparting MCF7 cells resistance against anti-cancer drug, cisplatin.