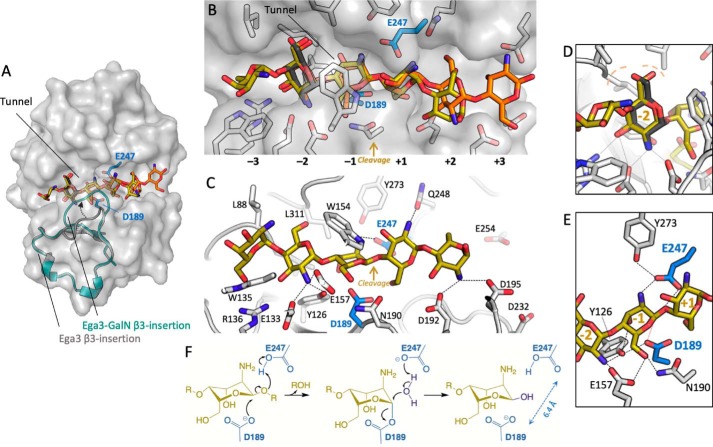
Figure 7.
In silico docking of α-1,4-(GalN)5 reveals six substrate-binding subsites. A, transparent surface representation of Ega3 structure with the galactosamine (dark gray) found in the crystal structure and the top two scoring conformations (no. 1 is yellow and no. 2 is orange). The β3-insertion is shown as a cartoon labeled with an arrowhead indicating the change between the apo structure (gray) and Ega3–GalN (teal). Putative catalytic residues are in blue. B, cartoon representation of the Ega3–GalN structure (white) and putative catalytic residues (blue). The galactosamine (dark gray) found in the crystal structure aligns with the top two scoring conformations (no. 1 is yellow and no. 2 is orange). The subsites are numbered with the putative site of cleavage between −1 and +1. C, side view of the lowest energy conformer (yellow) with residues that participate in binding the oligosaccharide labeled. Dashed lines indicate H-bonds and salt bridges to ligand amines. All interaction distances are less than 3.1 Å. D, saccharide in subsite −2 overlaps with the galactosamine (dark gray) in the Ega3–GalN structure and has an identical hydrogen bond network. The hydrophobic pocket created by Leu-88 and Leu-311 is indicated by the dashed light orange lines. E, Ega3 active site with the hydrogen bond network is indicated by the dashed black lines. The catalytic nucleophile, Asp-189, is aligned to attack the anomeric carbon (red dashed line). F, proposed mechanism of Ega3 with D189 acting as the catalytic nucleophile.