Figure 1.
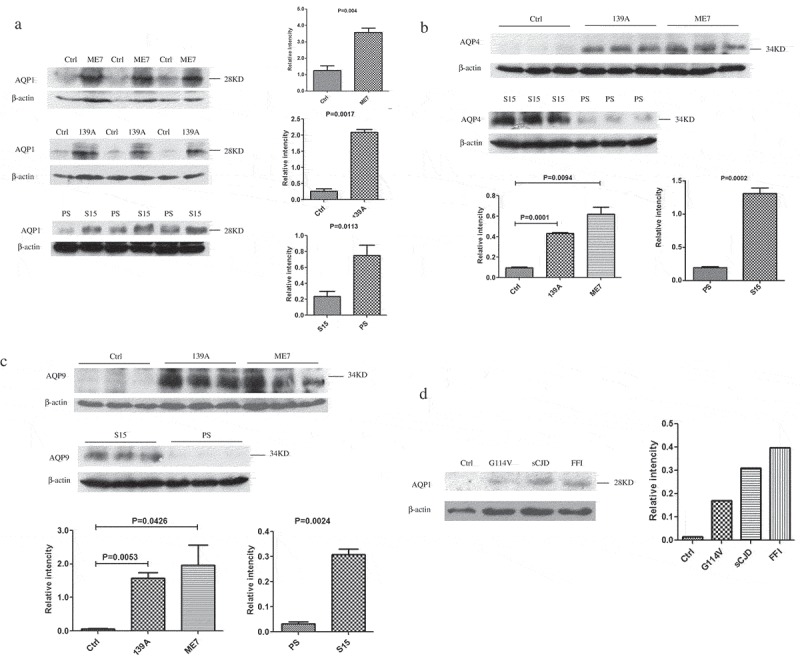
Increased levels of AQP1, AQP4 and AQP9 in the brain tissues of various prion diseases. The levels of three AQP isoforms in the brain homogenates were evaluated by Western blots with the individual antibodies. (a). AQP1 in the brains of scrapie-infected mice. (b). AQP4 in the brains of scrapie-infected mice. (c). AQP9 in the brains of scrapie-infected mice. Three mice infected with scrapie agent 139A, ME7 or S15 were employed, while three age matched mice and three mice inoculated with the lysate of SMB-PS cells were used as control. (d). AQP1 in the homogenates from frontal lobes of various human prion diseases, including sCJD, FFI and G114V-gCJD. β-actin was used as an internal control. The densities of signals are determined by densitometry and showed as AQP/β-actin after normalized with the individual values of β-actin. Graphical data denote mean+SD. Statistical differences compared with controls are illustrated on the top.
