Figure 2.
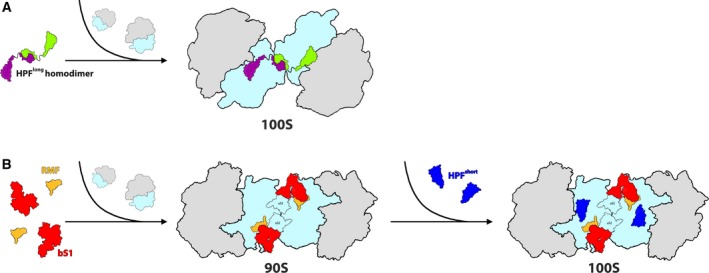
Overview of hibernation modes across bacteria. (A) 100S Ribosome formation is mediated by the binding of HPFlong‐NTD (colored in green and purple to differentiate between each HPF molecule which binds to a different ribosome) to the ribosomal SSU (colored in light blue). Dimerization of the two ribosomes is facilitated by homodimerization of two HPFlong‐CTDs. Secondary contacts may involve other ribosomal components, depending on the species. LSU is colored in gray. (B) Ribosome hibernation in Escherichia coli (and other γ‐proteobacteria). The initial binding of RMF and rProtein bS1 (colored in yellow and red, respectively) to the ribosome induces the formation of the immature 90S complex. Later HPFshort (colored in blue), binds at the catalytic site of the SSU (colored in light blue), resulting in the formation of the hibernating 100S dimer. LSU is colored in gray.
