Figure 2. Experimental application of CRISPR-Cas9 in elucidating the role of PKCδ in neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation.
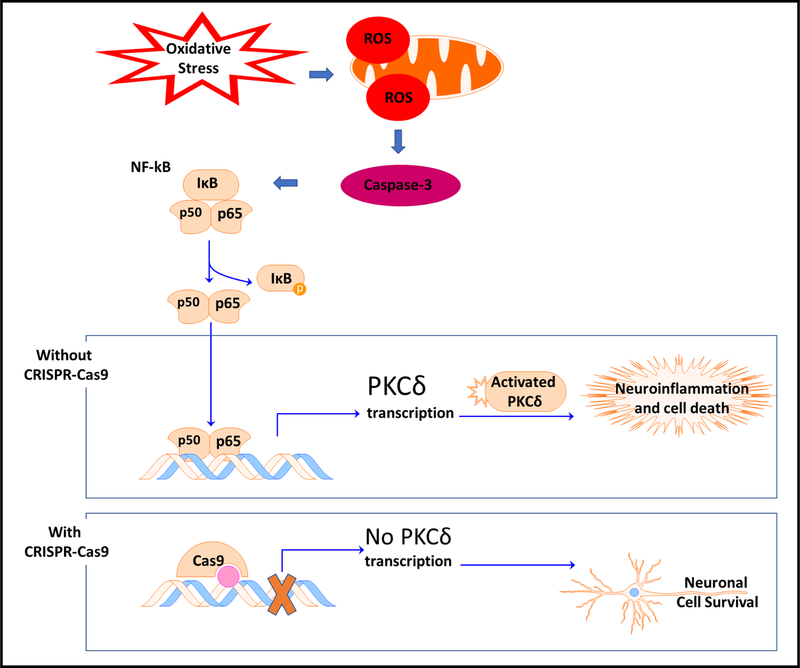
Oxidative stress-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) can lead to activation of caspase-3, which induces the phosphorylation of inhibitor of κB (IκB), causing nuclear translation of the p50/p65 complex. In the nucleus, it participates in the transcription of PKCδ, which can be proteolytically cleaved, thereby inducing neuroinflammation and neuronal cell death. However, CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of PKCδ made cells more resistant to oxidative stress-induced cell death.
