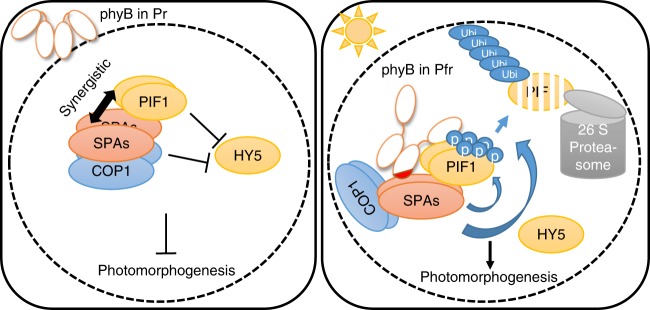
Fig. 9.
Model showing phyB-SPA1-COP1-PIF1 relationships in dark and light conditions. In darkness, inactive Pr form of phyB is present in the cytoplasm, while COP1-SPA complex together with PIF1 as a co-factor induces degradation of positively acting transcription factors (HY5/HFR1 and possibly others). However, upon light exposure, activated Pfr form of phyB translocates into the nucleus and interacts with PIF1 as well as SPA1 to trigger rapid phosphorylation of PIF1. phyB interacts with PIFs mostly through its N-terminal domain, while its extreme C-terminal 80 amino acids (shown as a red patch) are necessary for SPA1 interaction. By stabilizing the phyB-SPA1-PIF1 tripartite complex, phyB can initiate the light-induced phosphorylation of PIF1 by SPA1 kinase. Phosphorylated PIF1 is then recognized by the CUL4COP1-SPA E3 ubiquitin ligase for rapid poly-ubiquitination and subsequent degradation through the 26S proteasome. Degradation of PIFs and stabilization of HY5 result in promotion of photomorphogenesis