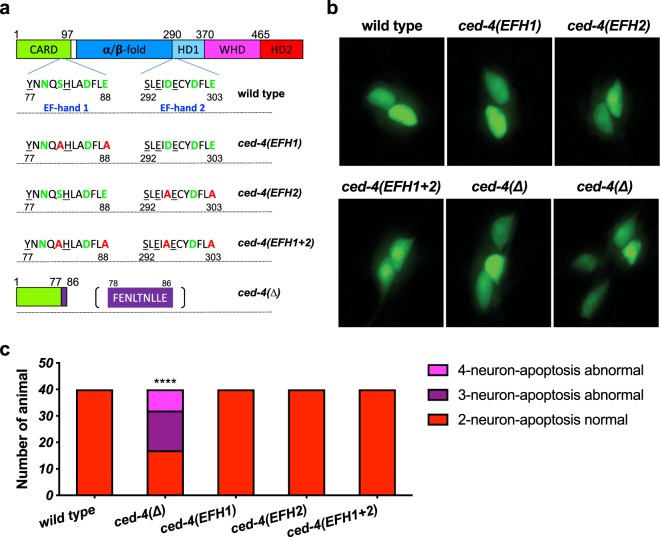
Figure 1.
CED-4 EF-hand mutations do not disrupt CED-4 apoptosis functions. (a) Amino acid substitutions in the predicted CED-4 Ca2+-binding domains, EF-hand 1 (EFH1) and EF-hand 2 (EFH2) were introduced via CRISPR genome editing. Amino acids labeled green are potential Ca2+-binding amino acids; in each domain, we replaced two of these residues with alanine (red label). ced-4(∆) is a likely null allele that could potentially only express a partial CARD domain followed by a random short sequence (labeled purple). Actual allele names are: EFH1 ced-4(bz401); EFH2 ced-4(bz410); EFH(1 + 2) ced-4(bz406); ∆ced-4(bz404); CARD: caspase recruitment domain; HD: Helical domain; WHD: Winged-helix domain. (b) Representative pictures of the tail touch receptor neurons labeled by Pmec-4GFP in the background of various ced-4 alleles. In WT, two PLM tail neurons survive; in ced-4 null mutants, as many as two additional neurons survive and differentiate, so 3–4 cells may be visualized. (c) The PLM tail touch receptor neuron count for ced-4 mutants, n = 40 animals for each group in one trial. ****p < 0.0001 as compared to the wild type, Chi-square test.