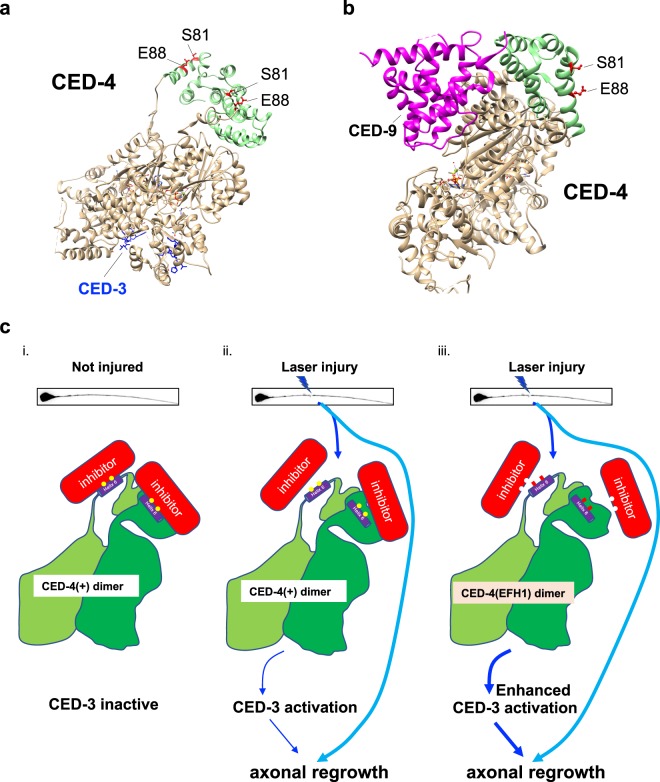
Figure 5.
CED-4 S81 and E88 face away from the CED-3 or CED-9 interaction sites that regulate apoptosis, but might be available to interact with a factor that licenses transient CED-3 activation for localized repair. (a) Ribbon structure shows a CED-4 dimer (most residues in tan, but CARD domain in green with S81 and E88 highlighted in red), with two interacting CED-3 fragment residues (indicated in blue) as determined from a crystal structure. Note that the CARD domain is positioned apart from the CED-3 interaction domain and that S81 and E88 are oriented away from the main structure such that the subdomain that includes S81 and E88 might interact with another protein (or another region of a dynamic CED-4). (b) Ribbon structure shows a partial CED-4 dimer with one CARD domain depicted (CARD domain green, with S81 and E88 in red), binding to the CED-9 protein (magenta). Note that the CARD domain helix 6 containing S81 and E88 is positioned apart from the CED-9 interaction domain, with those AA positions facing outward from the protein. (c) A proposed model of CED-4 non-apoptotic function in neuronal repair shows (i) the two essential amino acids (S81 and E88 shown as yellow dots) in CED-4 helix 6 binding to a hypothetical inhibitor (red, indicated as a protein but could be an ion-binding site associated with conformational change); two green shades of CED-4 represent S and L isoforms. Upon injury (ii), the inhibition might be transiently relieved, enabling CED-4 to locally activate CED-3 caspase. Note that known apoptosis inhibitor CED-9 binds to the opposite side of the CARD helix 6 domain and is unlikely to be directly involved at the helix 6 sites. (iii) The substitution of alanine for S81 and E88 may reduce the affinity of the inhibitor to bind to the CED-4 dimer and subsequently increase the capacity to activate CED-3 in response to injury stress. When S81 and E88 in the CARD domain are absent, the interaction with the inhibitor is weakened and regeneration outgrowth is increased in a CED-3 caspase-dependent mechanism under injury conditions.