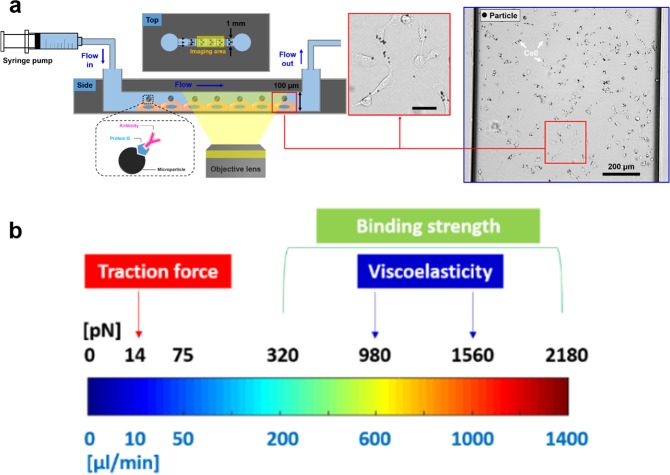
Figure 1.
The traction force, viscoelastic properties, and bond strength of the dorsal side of cells were evaluated using the microfluidic device at high-throughput. (a) Cells are seeded in a microfluidic channel and then particles coated with ligand targeting surface molecules are added to bind to the cell surface. To induce hydrodynamic forces, a syringe pump and tubing are used. Particle-bound cells are shown in the inset marked (red box, Scale bar: 50 μm). Whole field of view of actual image taken for highthroughput analysis was shown (blue box). Black dots indicate particles attached to cells (white arrows). (b) Force spectrum is shown as a function of flow rate. Different flow rates can be applied for various types of measurement. For example, to measure the traction force, a force in the range of tens of pN is used. To measure the viscoelastic properties, forces of in the range of 1 nN are used. To measure the bond strength, a varied force which increases in a stepwise manner is used, ranging from ~300 pN to ~2000 pN.