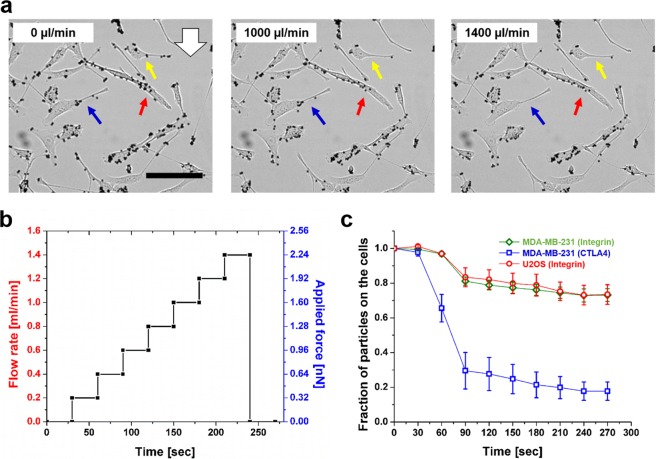
Figure 4.
The rupture force between ligand-receptor bond can be measured in situ at the dorsal side of the cell using high flow rates. (a) Particles increasingly detach from the cells as the flow rate increases. For example, the ligand-receptor bond rupture can be observed in the cells indicated by the yellow, red, and blue arrows. White arrow indicates flow direction. Scale bar: 100 μm. (b) Particles bound to the cells are imaged over 270 seconds when subjected to incremental flow rates and the resulting applied forces. The flow rate was increased step-wise (step size = 200 μl/min, 30 seconds/step). (c) The number of cell-bound particles decreases as the flow rate and the resulting applied forces increase. The rupture forces of integrin-antibody bond and the CD80-CTLA4 bond are measured. The sharp drop of the particle number is observed in the case of CD80-CTLA4 at 200 µl/min, indicating approximately 320 pN of force is required to disrupt the bond formed between CD80 and CTLA4 at the cell surface. In the case of integrin-antibody, the measurement results from MDA-MB-231 and U2OS cells are consistent, where ~27% of the bond population are disengaged by forces of ~640 pN (400 µl/min).