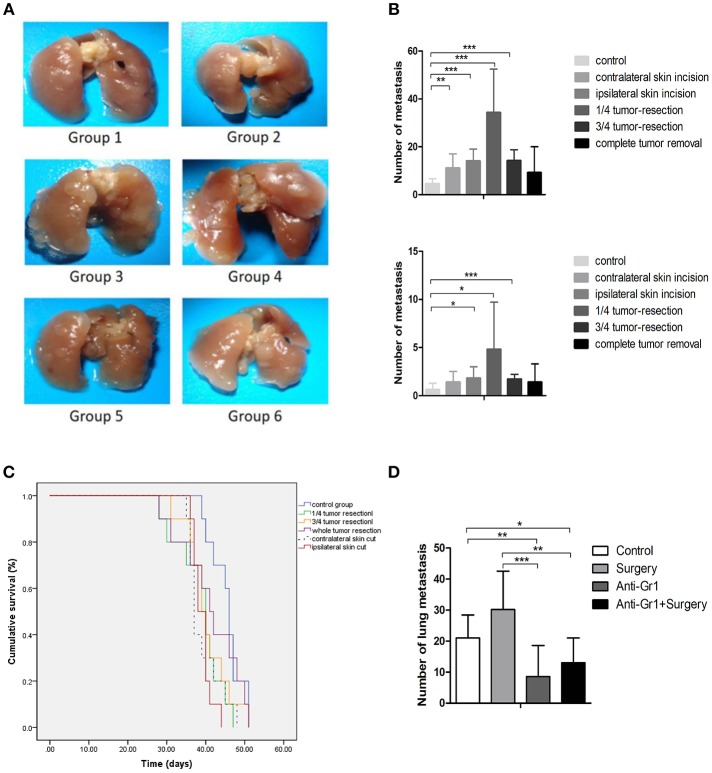
Figure 1.
(A) Pulmonary metastases of the mice killed on the 28th day after inoculation. Group 1: control group; 2: contralateral skin incision group; 3: ipsilateral skin incision group; 4: 1/4 tumor resection group; 5: 3/4 tumor resection group (resect a large part of the tumor, simulating the effect of subtotal resection on tumor metastasis and tumor microenvironment); 6: whole tumor resection group; (B) Quantification of pulmonary metastasis: (i) Total number of metastatic nodules; (ii) The number of metastatic nodules of diameters ≥3 mm; (C) The survival outcomes of the six groups (n = 10) recorded 2 days after the initial procedure (day 0 is inoculated date); (D) The quantification of pulmonary metastases in each group to study the effect of anti-Gr1 treatment on lung metastasis. Mice were divided into four groups: the control group, surgery group (1/4 tumor resection), anti-Gr1 group (The clearance of MDSCs was achieved with anti-Gr1 antibody three times), and anti-Gr1+ surgery (1/4 tumor resection) group. Mice went through surgical removal of tumors on the 10th day after inoculation and were sacrificed on the 28th day for the quantification of lung metastasis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.