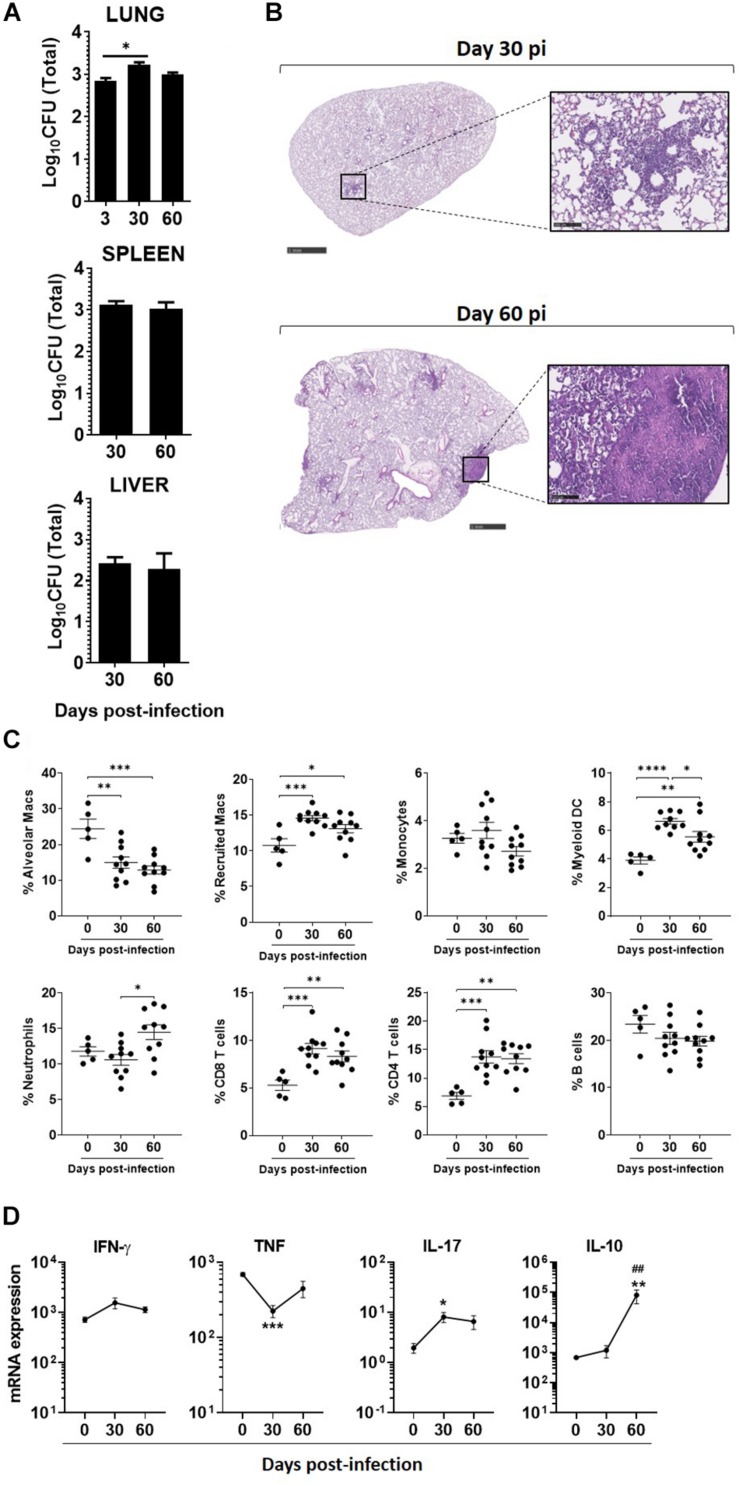
FIGURE 2.
Mycobacterium africanum infection is controlled by immunocompetent hosts, with minimal pathology and immune responses. C57BL/6 mice were infected via aerosol with a high dose (>500 CFU) of M. africanum. (A) At the indicated time points, the lungs, spleens, and livers of infected mice were collected and the bacterial burden determined by CFU enumeration. Lungs were harvested at the indicated time points and (B) pathology determined by H&E staining; (C) immune cell populations determined by flow cytometry; and (D) the expression of the indicated cytokines measured by real-time PCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from at least two independent experiments with five animals each. The images in (B) are of one animal representative of the experimental group. Scale bar on the left and right images correspond to 1 mm and 100 μm, respectively. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test was used to perform the statistical analysis. ∗p < 0.05; ∗*,##p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Asterisk (∗) related to differences compared to NI mice, and hash (#) related to differences comparing d30 to d60 post-infection.