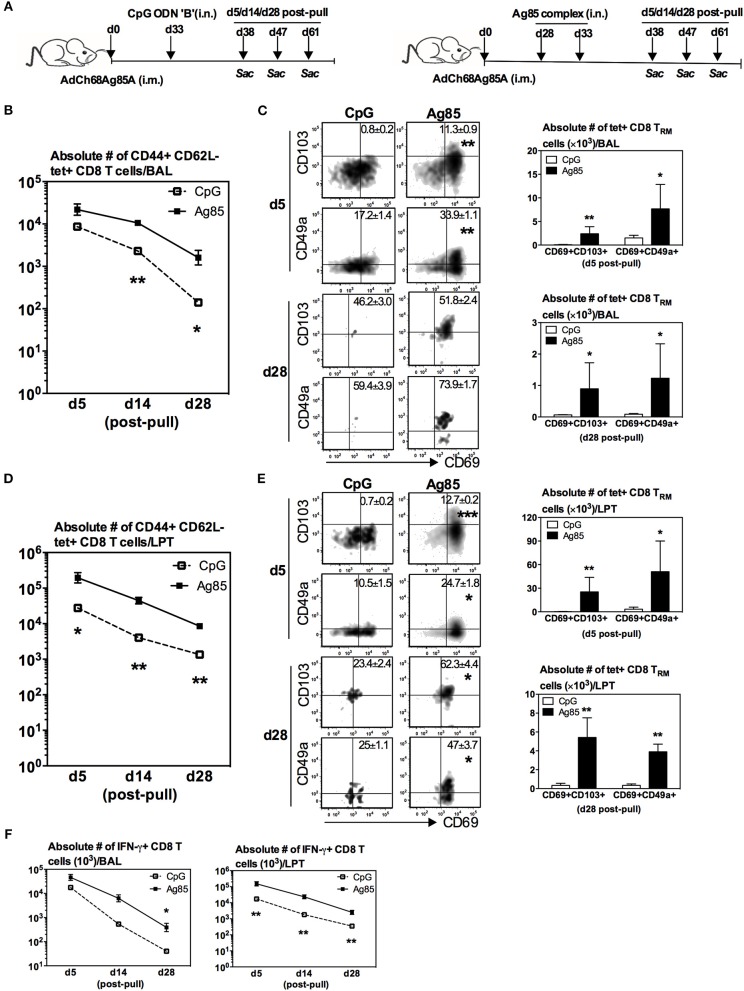
Figure 2.
Induction of Ag-specific CD8 TRM by cognate Ag-, but not by CpG-based RM-pull strategy during the memory phase of T cell responses to parenteral immunization. (A) Experimental schema. Mice were immunized i.m. with AdCh68Ag85A. At day 28 post-immunization, mice were administered i.n. with CpG (single dose) or Ag85 complex (two doses 5 days apart). Mice were then scarified at specified time points (day 5, day 14, day 28) post-RM-pull and mononuclear cells from BAL fluids and lungs were subjected to Ag85A tetramer and CD8 TRM surface marker or intracellular cytokine immunostaining. (B) Line graphs showing kinetic changes in numbers of tetramer+ cells in the airway. (C) Representative dotplots showing frequencies of tetramer+ CD8 T cells co-expressing CD69 and CD103, or CD69 and CD49a, and bar graphs showing numbers of tetramer+ CD8 T cells co-expressing CD69 and CD103, or CD69 and CD49a in the airway at day 5 and day 28 post-RM-pull. (D) Line graphs showing kinetic changes in numbers of tetramer+ cells in the lung parenchymal tissue (LPT). (E) Representative dotplots showing frequencies of tetramer+ CD8 T cells co-expressing CD69 and CD103, or CD69 and CD49a, and bar graphs showing numbers of tetramer+ CD8 T cells co-expressing CD69 and CD103, or CD69 and CD49a in LPT at day 5 and day 28 post-RM-pull. (F) Absolute numbers of interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-producing CD8 T cells in the airway and LPT. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. of three mice/group/time point, representative of two independent experiments. *P< 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with CpG group.