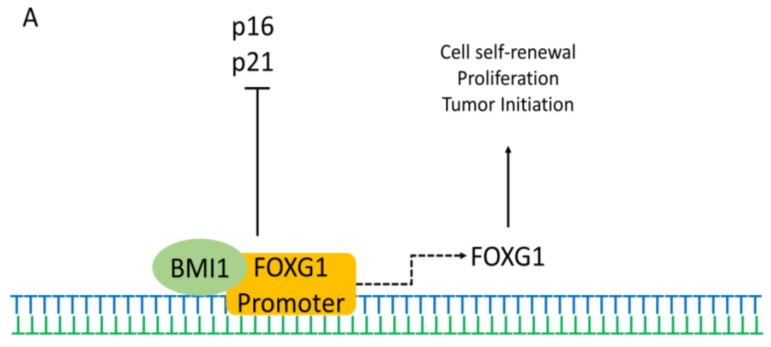
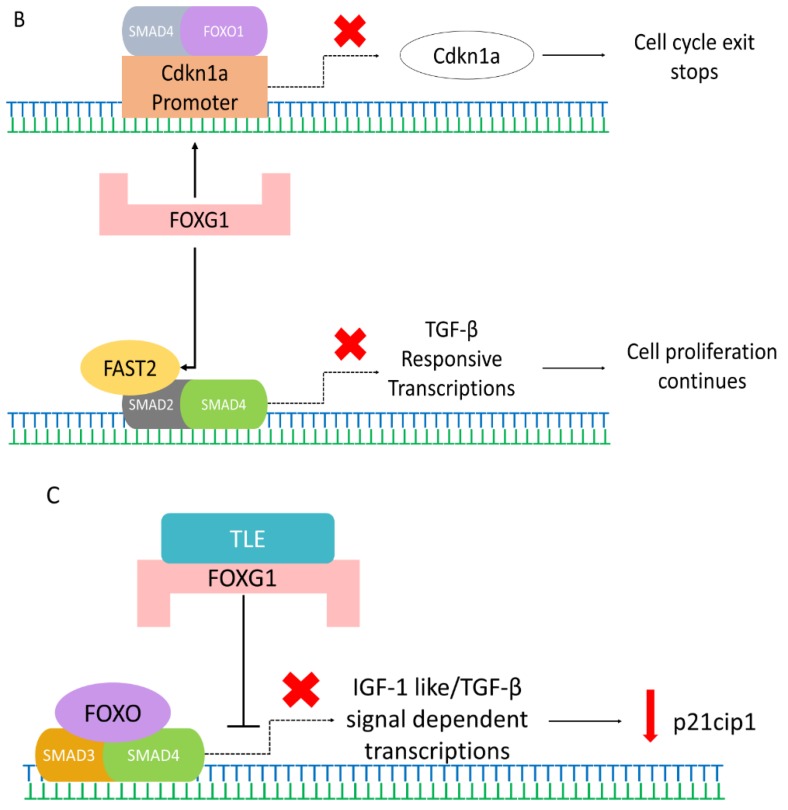
Figure 2.
Possible pathways of FOXG1 controlling the different mechanisms in the cell. (A) BMI1 (green) interacts and cooperates with FOXG1 promoter (orange), which initiates FOXG1 expression. This interaction also controls cell self-renewal, proliferation, differentiation, and tumor growth. Simultaneously, it also inhibits cell cycle inhibitors p21 and p16. (B) FOXG1 (pink) inhibits the expression of Cdkn1a by associating and attaching to the SMAD4 (grey) and FOXO1 (purple) complexes at Cdkn1a promoter to prevent the cell cycle exit and stop differentiation. Also, FOXG1 interacts with FAST2 to inhibit the FAST2 (yellow)-SMAD2 (dark grey)-SMAD4 (green) complex formation, thereby repressing the TGF-β responsive transcriptions and allowing cell proliferation. Cross (red) indicate the transcriptional loss. (C) TLE-FOXG1 complex represses the FOXO (purple)-SMAD3 (orange)-SMAD4 (green)-mediated transcription of p21cip1 initiated by IGF-1like/TGF-β signal, which inhibits apoptosis while promotes growth and proliferation.