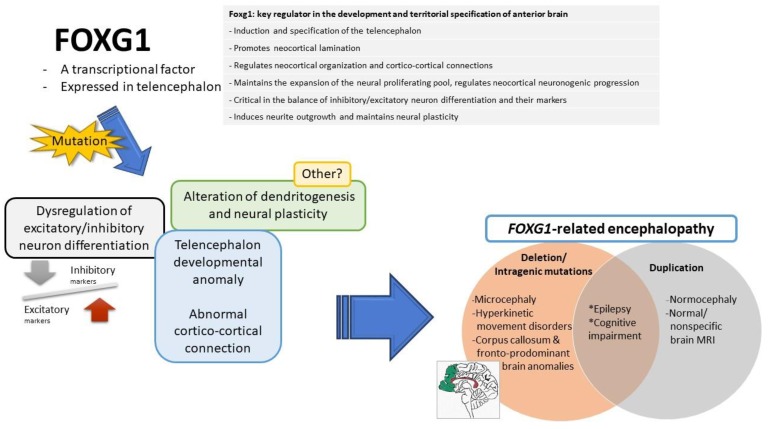
Figure 4.
The possible functions of FOXG1 (right upper), which have been demonstrated in in vivo animal models: The mutations of FOXG1 gene may lead to possible pathological events (left), including dysregulation of excitatory/inhibitory neuron differentiation, telencephalon developmental anomaly, abnormal cortico-cortical connection, and alteration in dendritogenesis and neural plasticity. These may be the underlying possible pathomechanisms leading to FOXG1-related encephalopathy (right lower).