Figure 2.
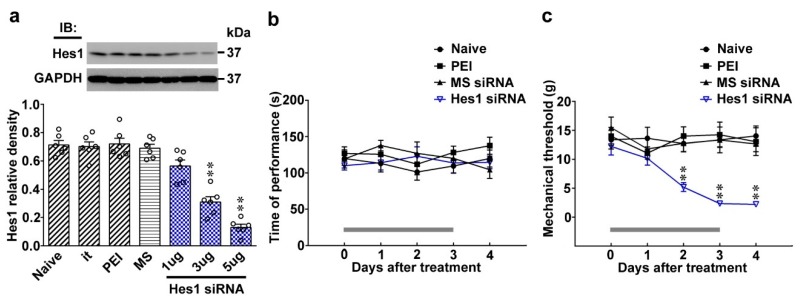
Focal knockdown of spinal Hes1 expression elicits no motor deficits but provokes behavioral allodynia. (a) Representative Western blot and statistical analyses (normalized to GAPDH) showing the Hes1 levels in the dorsal horn dissected from naïve animals (Naïve) were not affected by implantation of an intrathecal catheter alone (it) or spinal administration with polyethylenimine (PEI, 10 μL; daily for 4 days) or missense siRNA (MS siRNA, 5 μg, 10 μL; daily for 4 days) but was dose-dependently decreased by intrathecal administration with Hes1 siRNA (Hes1 siRNA; 1, 3, and 5 μg; 10 μL; daily for 4 days) at day 4 after the start of treatments. IB, Immunoblotting. One-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (6,35) = 47.9, p < 0.0001. ** p < 0.01 vs. Naïve. n = 6. (b) Rota-rod test demonstrating no statistical difference in the motor performance among naïve animals as well as naïve animals administered with polyethylenimine, missense siRNA, or Hes1 siRNA (5 μg, 10 μL). The gray bar at the bottom indicates the duration of the reagents’ administration. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures over time, treatment, F (3,24) = 1.170, p = 0.3419; time, F (4,96) = 0.2094, p = 0.9327; treatment × time, F(12,96) = 0.8289, p = 0.6205. n = 7. (c) Results of the von Frey test demonstrating that administration to naïve rats with Hes1 siRNA (5 μg, 10 μL), but not polyethylenimine, or missense siRNA decreased the withdrawal threshold of the hind paw at days 2, 3, and 4 after the injection. The gray bar at the bottom indicates the duration of the reagents’ administration. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures over time, treatment, F (3,24) = 40.16, p < 0.0001; time, F (4,96) = 2.481, p = 0.0489; treatment × time, F (12,96) = 2.226, p = 0.0160. ** p < 0.01 vs. Naïve. n = 7.