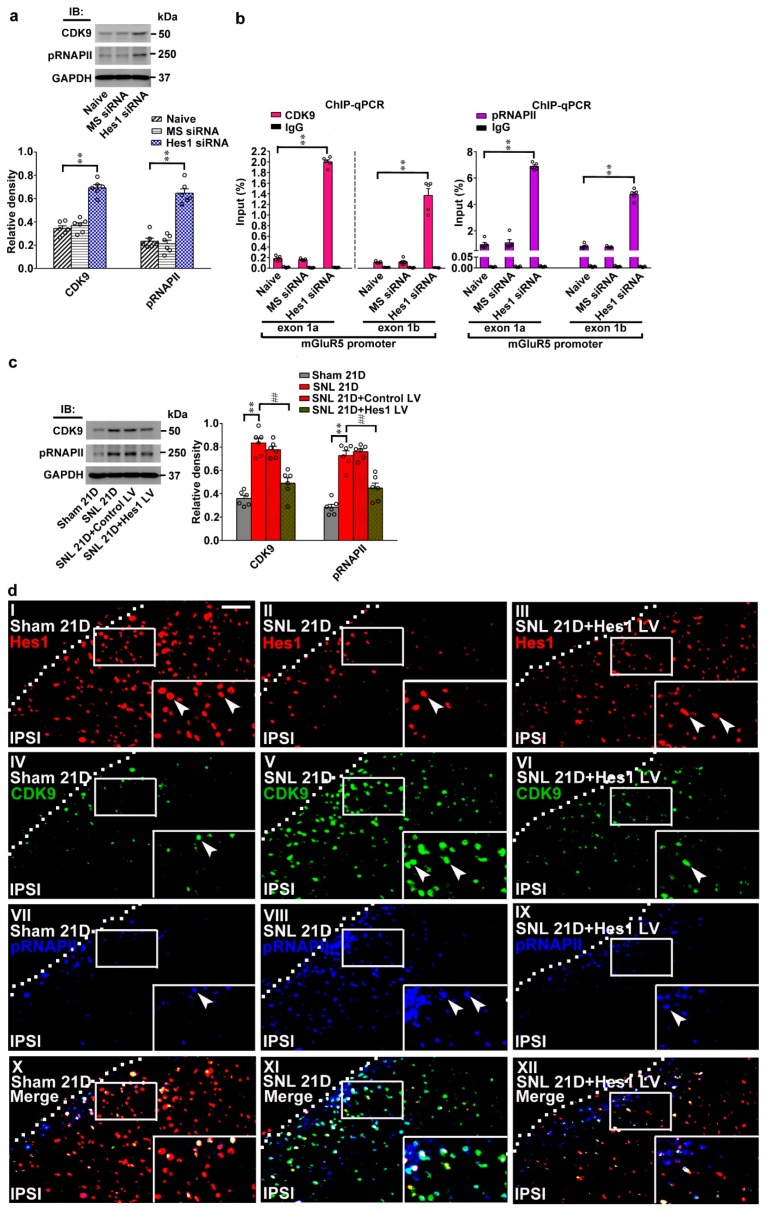
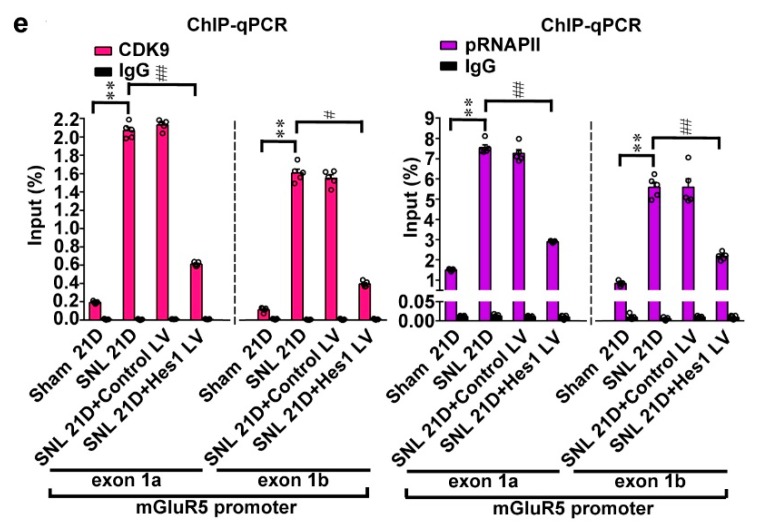
Figure 5.
Neuropathic injury impedes Hes1-suppressed CDK9 recruitment and RNAPII phosphorylation on mGluR5 promoters. (a) Representative western blot and statistical analyses (normalized to GAPDH) of dorsal horn samples demonstrating the levels of CDK9 and phosphorylated RNAPII (pRNAPII) were increased by spinally administering naïve animals (Naïve) with Hes1-siRNA but not with missense siRNA (Hes1 siRNA and MS siRNA, respectively, 5 μg, 10 μL; daily for 4 days). IB, immunoblotting. CDK9, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (2,15) = 64.17, p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (2,15) = 59.83, p < 0.0001. ** p < 0.01 vs. Naïve. n = 6. (b) ChIP-qPCR assay of dorsal horn samples demonstrating that administering naïve animals with Hes1 siRNA, but not missense siRNA (Hes1 siRNA and MS siRNA, respectively. 5 μg, 10 μL; daily for 4 days), increased amounts of both CDK9 and pRNAPII antibody-precipitated exon 1a and exon 1b promoter fragments of mGluR5. CDK9, exon 1a, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (2,12) = 1494, p < 0.0001. CDK9, exon 1b, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F(2,12) = 88.97, p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, exon 1a, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (2,12) = 358.4, p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, exon 1b, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (2,12) = 373.5, p < 0.0001. ** p < 0.01 vs. Naïve. n = 5. (c) Representative western blot and statistical analyses of dorsal horn samples dissected at day 21 after operation. When compared with the sham operation (Sham 21D), spinal nerve ligation (SNL 21D) increased spinal CDK9 and pRNAPII levels; that were both reversed by administering SNL animals with Hes1-encoding vector (SNL 21D + Hes1 LV) but not the control vector (SNL 21D + Control LV). CDK9, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,20) = 38.06, p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,20) = 43.90, p < 0.0001. ** p < 0.01 vs. Sham 21D. ## p < 0.01 vs. SNL 21D. n = 6. (d) Immunofluorescence images of spinal slices dissected at day 21 post operation. Compared with the sham operation (left), SNL (middle) decreased the number and distribution of the Hes1-positive (red) neurons but increased that of the CDK9-postive (green) and pRNAPII-postive (blue) neurons in the dorsal horn; these effects were all reversed by transfecting SNL animals with Hes1-encoding vector (right). Dashed lines indicate the margin of the dorsal horn. The inset images at the bottom are amplifications of the upper marked area, with arrows indicating the immunopositive neurons. Scale bar = 50 μm; Thickness = 30 μm. (e) ChIP-qPCR assay of dorsal horn samples dissected at day 21 post operation. When compared with the sham operation, SNL increased the amounts of CDK9 and pRNAPII antibodies-precipitated exon 1a and exon 1b promoter fragments of mGluR5; effects were both reversed by transfecting SNL animals with Hes1-encoding vector but not the control vector. CDK9, exon 1a, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,16) = 1812, p < 0.0001. CDK9, exon 1b, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,16) = 675.6, p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, exon 1a, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,16) = 638.7 p < 0.0001. pRNAPII, exon 1b, one-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test, F (3,16) = 103.0 p < 0.0001. ** p < 0.01 vs. Sham 21D. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. SNL 21D. n = 5.