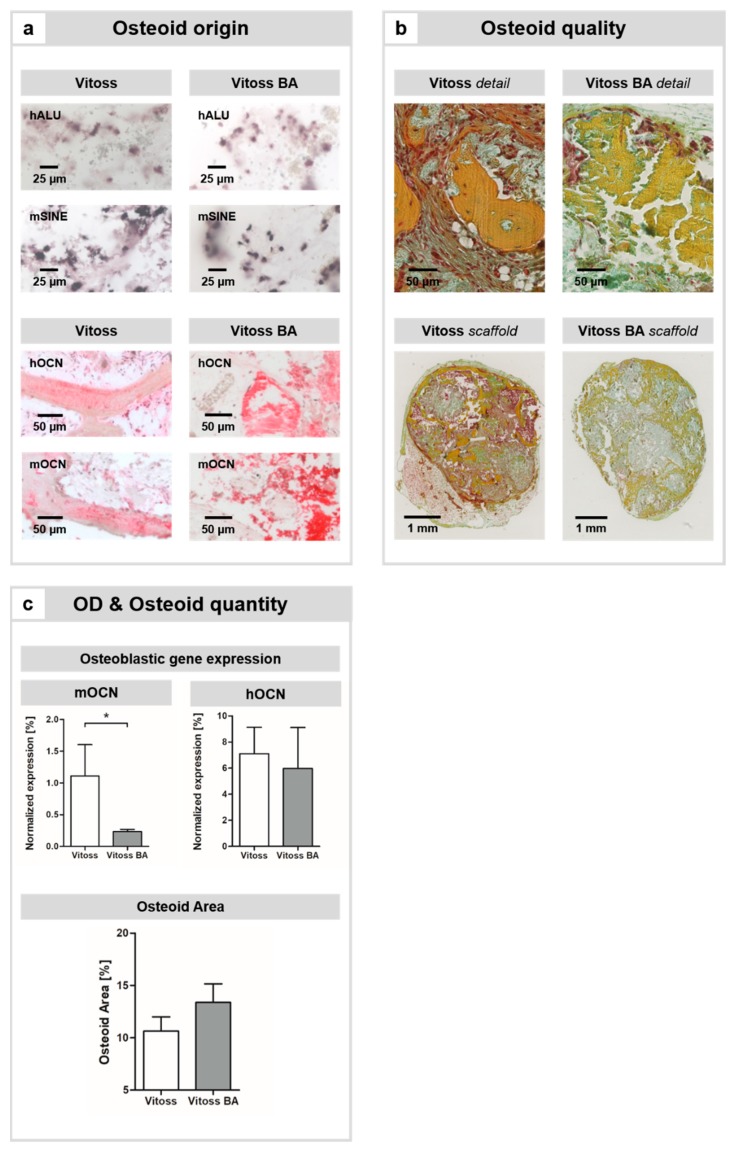
Figure 1.
Impact of BG particles on osteoid formation, maturation, and osteogenic cell differentiation (OD). (a) In both scaffold types, hybrid osteoid formation was detectable: The presence of murine and human cells was confirmed by in-situ hybridization for species-specific human repetitive genetic sequences, so-called short interspersed nucleotide elements (SINEs; murine: mSINE; human: hALU); positively stained cells appear in dark violet. Scale bars refer to 25 µm. Furthermore, human osteocalcin (hOCN) and murine osteocalcin (mOCN) were present in the osteoid, thus cells of both species committed to osteoid formation. Scale bars refer to 50 µm. (b) Qualitatively, osteoid maturation was further advanced in the Vitoss group, whilst slightly more osteoid was present in the Vitoss BA scaffolds (c). Scale bars refer to 50 µm for the detail view and 1 mm for the scaffold view, respectively. (c) Expression patterns of mOCN and hOCN as markers of osteogenic differentiation were assessed. (*) indicates significant differences.