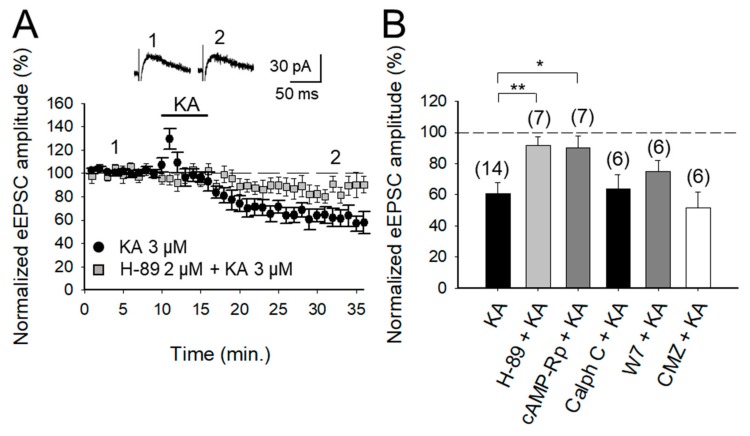
Figure 2.
Adenylyl cyclase (AC) and downstream protein kinase A (PKA) underly the KA-mediated depression of glutamate release in PF-PuC synapses. (A) Time-course of the effect of KA on eEPSC amplitude in control and H-89 treated slices. Inset shows representative traces showing that KA (3 μM) does not decrease the amplitude of the eEPSCs in H-89 treated slices. (B) Summary of results. Blockade of PKA by H-89 (2 μM) or cAMP-Rp (100 μM) prevented the depressive action of KA. Blockade of protein kinase C (PKC) with calphostin C (1 μM) had no effect on the KAR-mediated decrease of the eEPSC amplitude (when compared to the first bar, KA). Depression similar to non-treated slices was observed on eEPSC amplitude in slices treated with 25 μM W-7 or 1 μM CMZ. The number of slices (from two to three mice) is indicated in parentheses at the top of each bar. Results are expressed as means ± SEM (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01, ANOVA test).