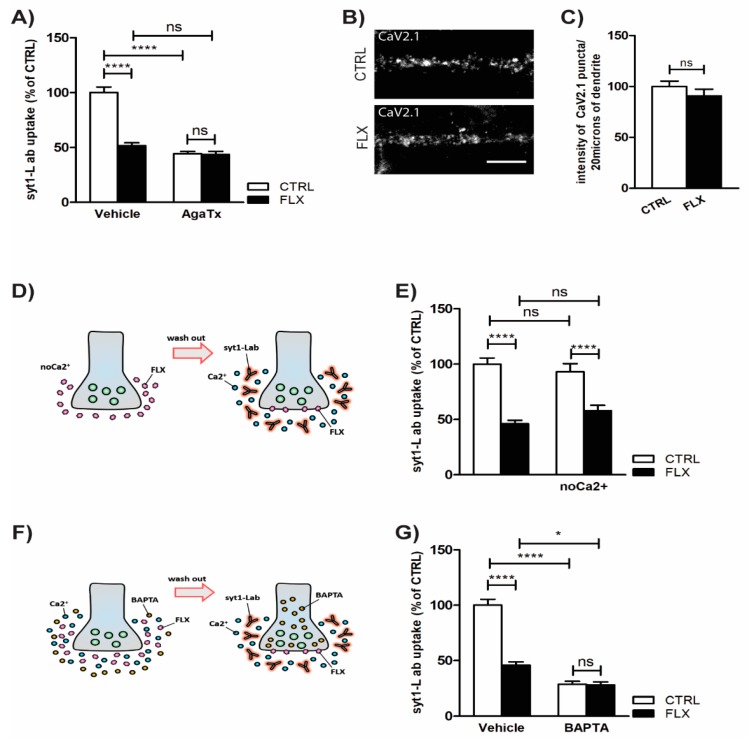
Figure 4.
Inhibition of P/Q type Ca2+ channels mediates FLX-induced suppression of presynaptic activity. (A) Statistical analysis of KCl-evoked syt1-L ab uptake from cortical neurons treated with CTRL solution or FLX (100 µM: 90 min) in the presence or absence of CaV2.1 channels antagonist (AgaTx; 0.4 µM) (n = 25 CTRL cells; n = 20 FLX; n = 28 AgaTx; n = 25 AgaTx/FLX). (B) Representative images of CTRL and FLX-treated cells stained with antibody against CaV2.1. (C) Quantification of (B) (n = 31 CTRL cells; n = 32 FLX-treated cells). (D) Schematic description and quantification (E) of KCl-evoked syt1-L ab uptake along 20 µm of proximal dendrite in cells treated for 90 min with CTRL solution or 100 µM FLX kept during the treatment in normal medium or Ca2+-free medium (n = 29 CTRL; n = 23 FLX; n = 29 no Ca2+; n = 29 no Ca2+/FLX). (F) Schematic description and statistical analysis (G) of KCl-driven syt1-L ab uptake from control (n = 29) and FLX-treated cortical neurons (n = 24) upon chelation of intracellular calcium by BAPTA-AM (10 µM) (n = 22 BAPTA-AM; n = 15 BAPTA-AM/FLX). In all graphs, values are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistic was done using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison test (A,E,G) or Student’s t-test (C); * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. Scale bar, 5 µm.