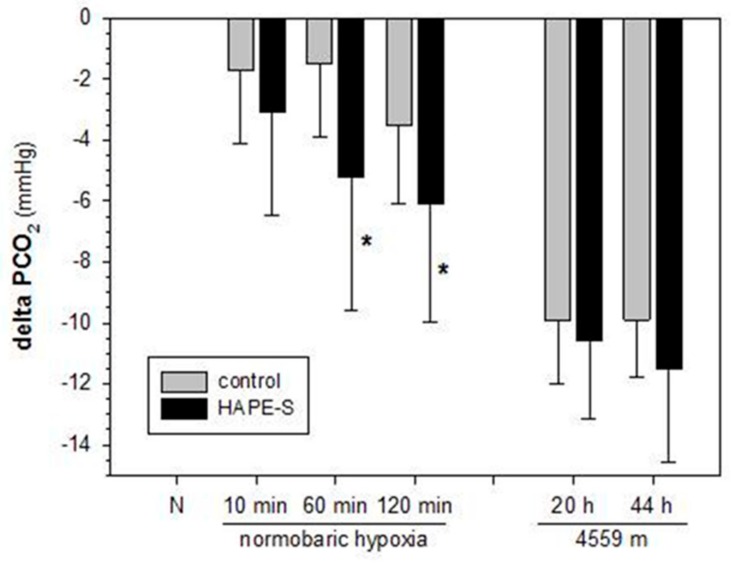
Figure 1.
Time-course of decrease in partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) in controls and high-altitude pulmonary edema –susceptibles (HAPE-S) in hypoxia. The decrease in PCO2 was calculated as the difference between normoxia and the time-points in hypoxia for the respective studies. Data for normobaric hypoxia (equivalent to 4550 m) are so far unpublished end-tidal PCO2 values from 15 controls and 17 HAPE-S from a study on the time course of change in systolic pulmonary arterial pressure reported in acute hypoxia reported in [17]). Data on high-altitude at the Capanna Margherita (4559 m) represent the arterial PCO2 on day 2 of the sojourn from 10 controls and 9 HAPE-S from a study reported in [2]. Mean values ± standard deviation. N normoxia; * indicate significant difference between controls and HAPE-susceptibles.