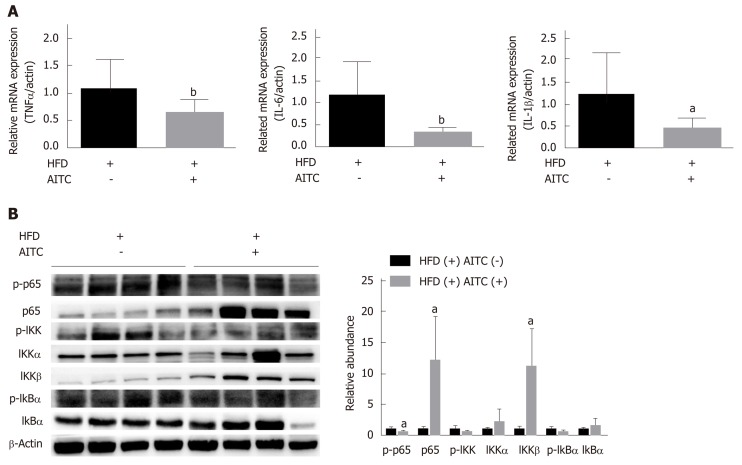
Figure 3.
Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates hepatic inflammation and inhibits the IκB kinase /nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in the liver tissues of high fat diet-fed mice. A: The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the liver of high fat diet (HFD)-fed control (n = 9) and HFD-fed allyl isothiocyanate (AITC)-treated mice (n = 10) were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. B: The protein expression of phosphorylated p65, p65, phosphorylated IκB kinase (IKK), IKKα, IKKβ, total and phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α (IκB α) in the liver was detected by western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs HFD(+) AITC(-). TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; HFD: High fat diet; AITC: Allyl isothiocyanate; p-p65: Phosphorylated p65; IKK: IκB kinase; IκBα: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B α.