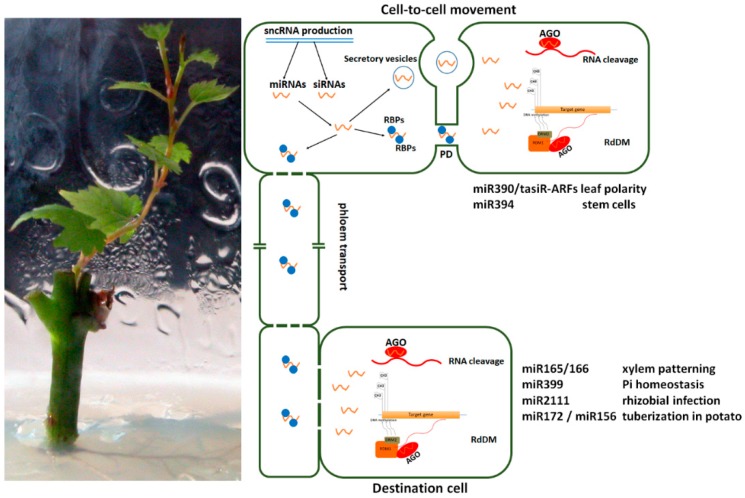
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of non-cell autonomous RNA delivery in plant tissues and potential biological activity in recipient cells. siRNAs and miRNAs can act as mobile signals moving cell-to-cell through plasmodesmata (PD), which establish cytosolic continuity between adjacent cells, and through vesicles resembling exosomes (hypothesis). Long distance trafficking of siRNAs and miRNAs, putatively complexed with protein associated to RNA (RBPs), takes place through the phloem stream, preferentially following the source-to-sink gradient. In recipient cells, the 21 to 22-nt long small RNAs incorporated into the ARGONAUTE 1 (AGO1) effector protein induce cleavage of complementary target mRNAs. The 23 to 24 nt long siRNAs loaded onto AGO 4 and/or 6 guide de novo DNA methylation (belonging to RNA directed-DNA methylation (RdDM) maintenance pathways) in a sequence-specific manner. The image on the left shows a micro-grafted grapevine plantlet grown under in vitro conditions.