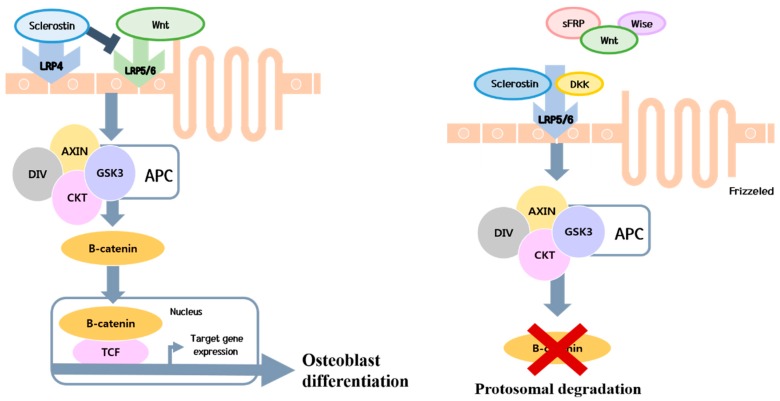
Figure 2.
Effects of sclerostin on osteoblast differentiation. Sclerostin produced by osteocytes inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling during early bone diseases in patients with cholestatic diseases [3]. This soluble protein is produced by osteocytes that differentiated from osteoblasts and prevents Wnt from binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins-5/6 (LRP5/6) transmembrane receptors. This blockade prevents Wnt signaling and osteoblast differentiation to inhibit bone formation. LRP: lipoprotein receptor-related proteins; GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3, DKK: Dickkopf; sFRP: secreted frizzled-related protein; APC: adenomatosis polyposis coli; TCF: T-cell specific transcription factor.