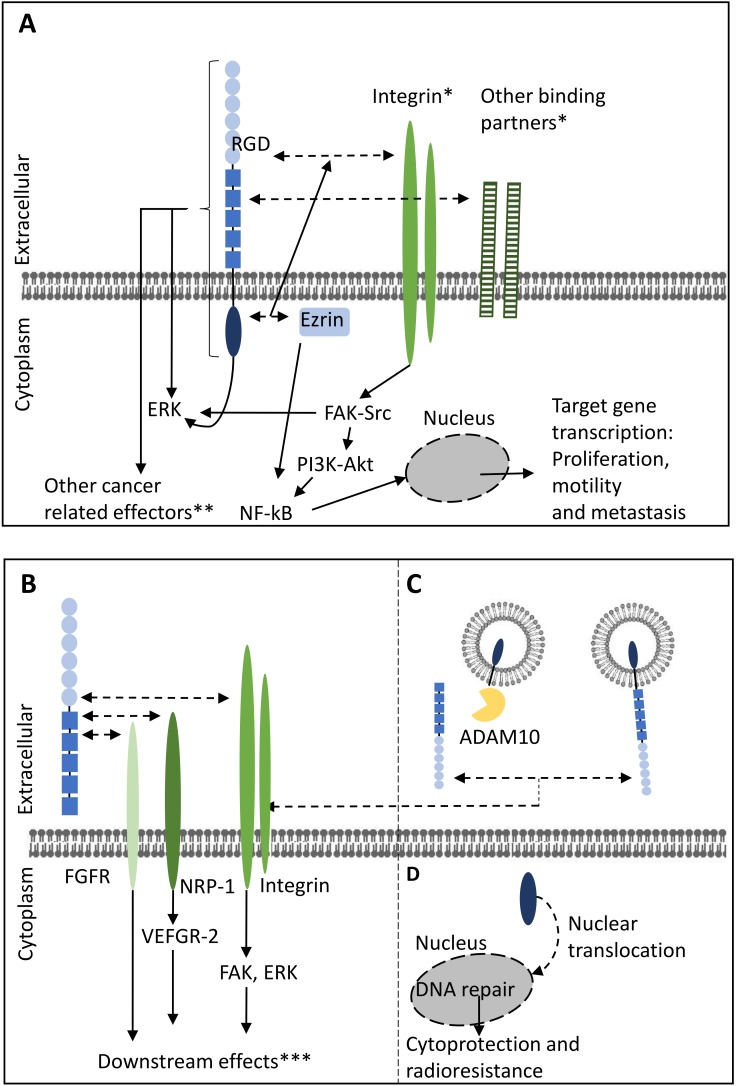
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of the signaling pathways of full-length L1CAM in the plasma membrane and soluble forms of L1CAM and contribution to cancer progression-associated events. (A) Full-length L1CAM in the plasma membrane. (B) Soluble ectodomain of L1CAM. (C) Exosomal L1CAM. (D) Intracellular L1CAM. * Interactions between L1CAM and binding partners can occur in cis as well as in trans (not depicted). ** For example, JNK, Wnt-related effectors and caspase 8. *** Such as cell motility, proliferation and angiogenesis. Solid arrows indicate induction of effects. Dashed arrows indicate interactions possibilities. ADAM: A Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein, Akt: protein kinase B, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, FAK: focal adhesion kinase, FGFR: fibroblast growth factor receptor, JNK: c-jun n-terminal kinase, MMPs: matrixmetalloproteinases, NF-κB: nuclear kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, NRP: neuropilin, PI3K: phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase, RGD: Arginylglycylaspartic acid, STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription, VEGFR: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, Wnt: wingless-related integration site.