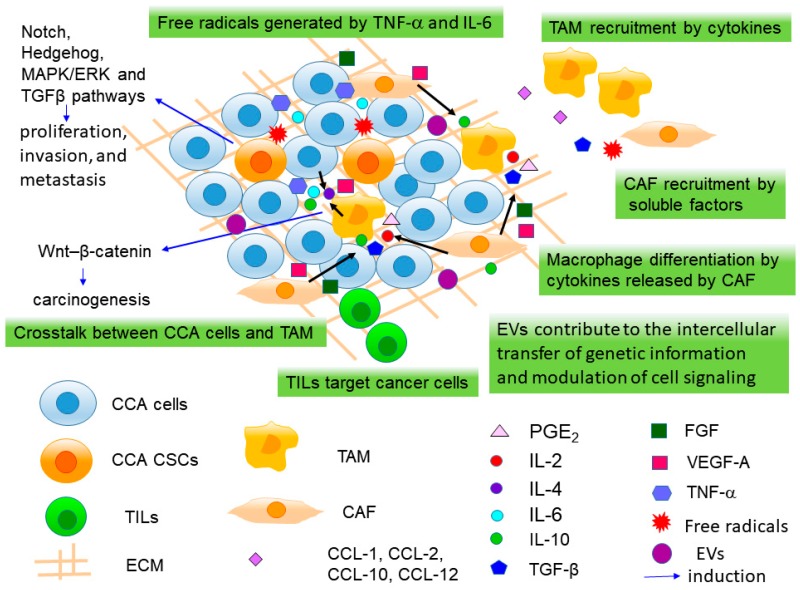
Figure 1.
The tumor microenvironment (TME), ‘Cancer stem cell (CSC) niche’ of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). The TME contains cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), cancer cells/CSCs, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and the extracellular matrix (ECM). TAMs are recruited into the TME by chemokines, MCP-1/CCL2, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)1, CXCL10 and SDF-1/CXCL12, secreted by tumor cells or other stromal cells. When infiltrating into TME, monocytes differentiate into M2 macrophages upon stimulation with soluble factors, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and cytokines, interleukin (IL)-2, IL-10 and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) released by CAF and other inflammatory cells. In the crosstalk between TAMs and CCA cells, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and TGF-β were secreted by lipopolysaccharide-activated TAMs. CAFs are recruited into the tumoral area and are activated by a variety of soluble mediators produced by both tumor cells, and the multiple inflammatory cells, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-D), TGF-β, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and FGF-2. CAF further recruit inflammatory cells, monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells to the tumor reactive stroma (TRS), through the secretion of VEGF, FGF, MCP-1/CCL2, SDF-1 and CXCL-14. TILs include CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, cytokine-secreting CD4+ T helper lymphocytes (Th), Forkhead box P3 (FoxP3)+ T leukocyte immunosuppressive regulators/regulatory T cells (Tregs), and B lymphocytes. TILs target cancer cells, and thus serve as a primary defence against cancer. T cell activation is tightly regulated by immune checkpoint pathways. TNF-α and IL-6 promote the generation of free radicals causing damage to DNA, resulting in genetic mutations and finally lead to tumor initiation. Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, Hedgehog, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and TGFβ pathways associated with cell growth dysregulation, invasion, and metastasis were activated surrounding CSCs. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play as carriers for the intercellular transfer of genetic information and modulation of cell signaling of cancer cells.