Figure 2.
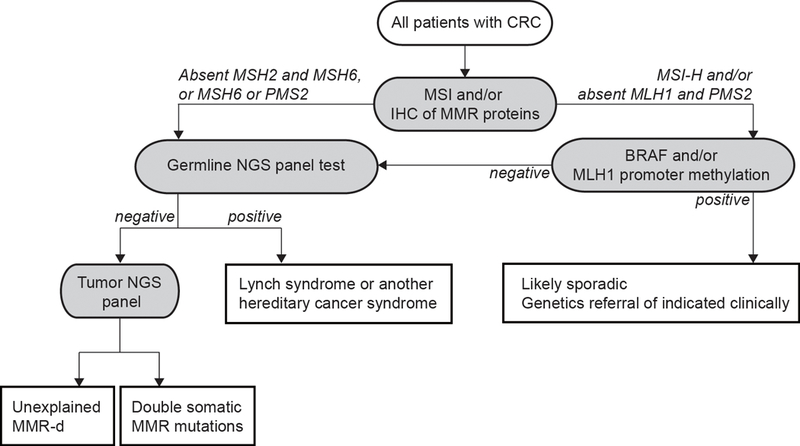
Strategy for universal tumor screening for Lynch syndrome in CRC patients (Adapted from Hampel et al. 2018 [29]). The different etiologies of MMR-d CRCs are: i) germline MMR gene mutation; ii) serrated pathway lesions (somatic BRAF mutation and/or MLH1 promoter hypermethylation); iii) double somatic MMR gene mutations; iv) somatic MMR gene mutation secondary to a POLE or POLD1 exonuclease mutation or to biallelic MUTYH mutations.
Abbreviations: CRC, colorectal cancer; IHC, immunohistochemistry; MMR, DNA mismatch repair; MMR-d, mismatch repair deficient; MSI, microsatellite instability; MSI-H, high level of microsatellite instability (microsatellite unstable); NGS, next generation sequencing.
