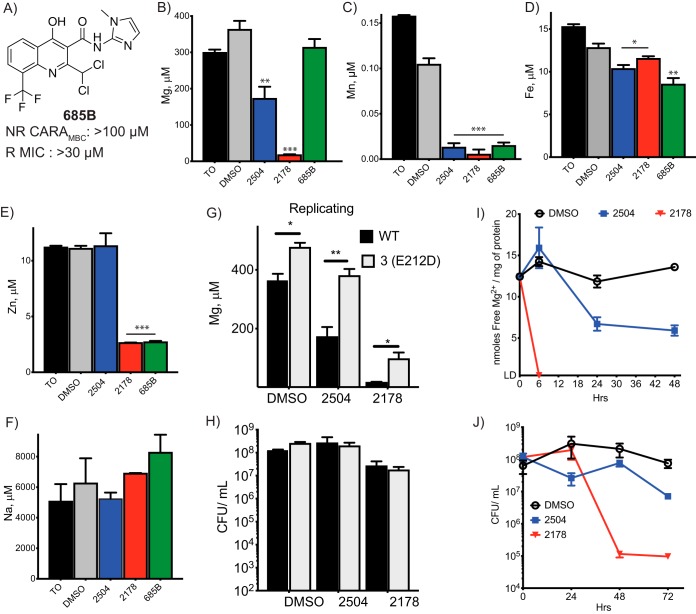
FIG 4.
Disruption of metallostasis in cells exposed to 4HQs. Approximately 109 replicating M. tuberculosis cells from WT and resistant strains were exposed to compounds at 25 μM for 24 h, including to the inactive 4HQ (A). Cells were harvested, and the total metal content was analyzed by ICP-MS for (B) magnesium, (C) manganese, (D) iron, (E) zinc, and (F) sodium. The method detects metals in both free and bound forms. Values are expressed as concentrations in the 30% nitric acid extract in which ppm (μg/ml) or ppb (ng/ml) were converted to μM. Comparison of (G) magnesium levels and (H) CFU/ml of WT and corA mutant 3(E212D). (I) Approximately 4 × 108 CFU/ml of M. tuberculosis were exposed to the indicated compounds at 25 μM for 6, 24, 48, or 72 h. Cells were harvested to measure labile intracellular levels of free Mg2+ by glycerol kinase assay and (J) the change in CFU/ml over time. Tests of statistical significance are indicated for comparisons between (B to F) WT M. tuberculosis treated with DMSO or the indicated compounds or (G) between WT and 3(E212D) M. tuberculosis in response to vehicle or compound exposure. *, P< 0.02; **, P < 0.002; ***, P < 0.0002. Data are means ± SD from one of two similar experiments, each in triplicate.