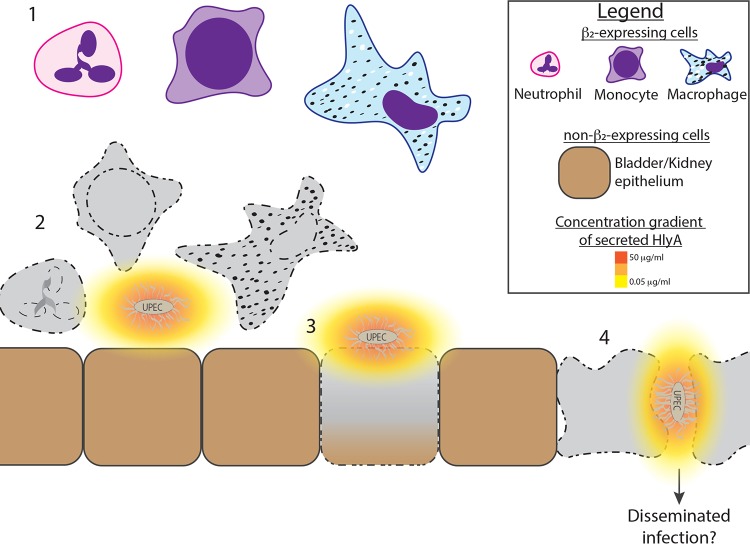
FIG 6.
Model for HlyA cytotoxic activity in infected tissue. (Part 1) A variety of leukocytes are recruited to the infected bladder/kidney. (Part 2) Secreted HlyA diffuses away from the UPEC bacteria and forms a gradient. β2-expressing leukocytes are sensitive to HlyA at low concentrations, where the toxin exhibits cytotoxic effects on the cells before they can effectively clear the bacteria, whereas non-β2-expressing epithelial cells remain viable at low concentrations of the HlyA. (Part 3) Non-β2-expressing epithelial cells are susceptible to cytotoxic effects of HlyA at high concentrations, likely at sites of adherent bacteria. (Part 4) Disruption of the epithelial cell barrier may lead to disseminated infection and severe complications from UTIs, like pyelonephritis and urosepsis.