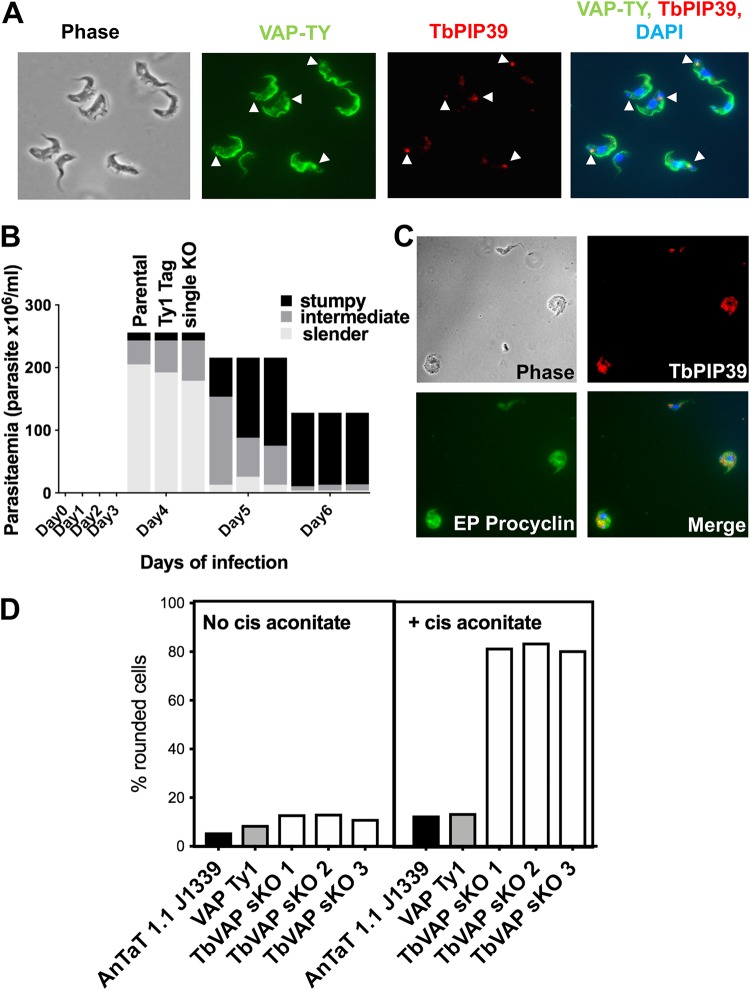
FIG 8.
(A) Detection of Ty1 epitope-tagged TbVAP in stumpy-form cells and its location with respect to TbPIP39. The Ty1-tagged TbVAP (green) is detected at the flagellar pocket region, along the flagellum attachment zone, and in the cell body. TbPIP39 (red) is closely proximal at the flagellar pocket region but not precisely coincident. DAPI (blue) denotes the position of the cell nucleus and kinetoplast. Arrowheads indicate the region of TbPIP39. Bar = 15 μm. (B) Proportion of slender, intermediate, and stumpy forms in TbVAP single-knockout cells versus parental cells or epitope-tagged TbVAP cells. (C) TbVAP single-allele-replacement mutants 24 h after the initiation of differentiation to procyclic forms. The differentiating cells (indicated by their expression of EP procyclin [green]) are swollen and lose integrity. TbPIP39 is punctate throughout the cell, indicating a glycosomal rather than periflagellar pocket distribution. The merged panel shows TbPIP39 (red), EP procyclin (green), and DAPI (blue) revealing the nucleus and kinetoplast. Bar = 25 μm. (D) Quantitation of cells that exhibit a rounded morphology. Parental T. brucei AnTat1.1 J1339 cells, TbVAP1-mNeonGreen-Ty1-expressing cells, or three TbVAP single-allele-deletion mutants (sKO) are shown. In each case, the percentage of rounded cells is shown after 24 h in either the absence or presence of cis-aconitate as a differentiation stimulus. At least 250 cells were scored for each cell line and each condition.