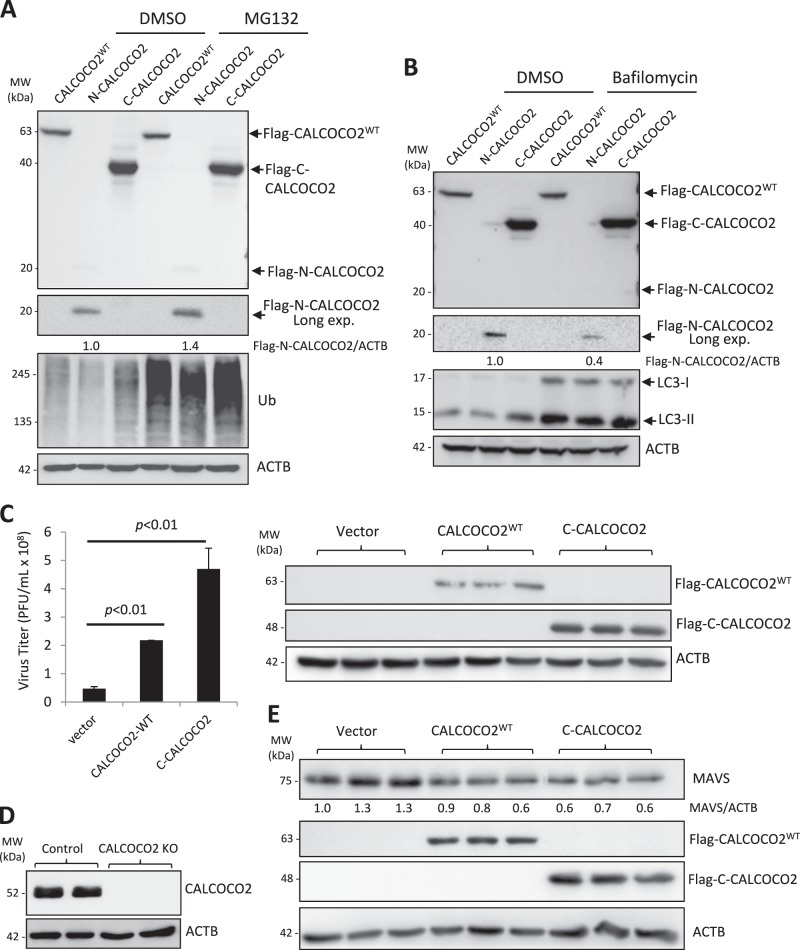
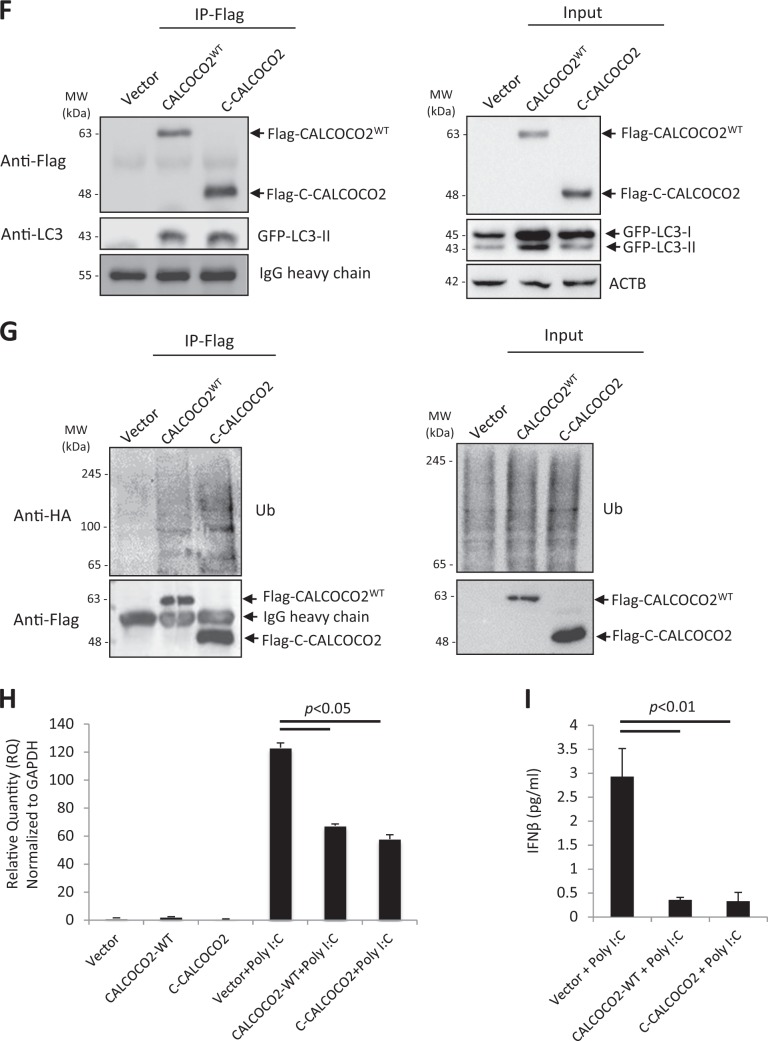
Fig. 7.
The C-terminal cleavage fragment of CALCOCO2 retains the function of full-length CALCOCO2 in promoting CVB3 growth. a, b HeLa cells were transfected with 3×FLAG-tagged CALCOCO2WT, N- or C-terminal cleavage fragments of CALCOCO2 (N-CALCOCO2 or C-CALCOCO2) in the presence of vehicle (DMSO), proteosomal inhibitor (MG132, 10 µM) (a), or lysosome inhibitor (bafilomycin, 200 nM) (b) for 6 h. Protein levels of full length and the respective cleavage fragments of CALCOCO2 were verified by western blotting with an anti-Flag antibody. Ubiquitin (a) and LC3 (b) were probed by western blotting to confirm the inhibition of proteasome and lysosome activities, respectively. Densitometry was conducted as in Fig. 1. c HeLa cells were transfected with 3×FLAG-tagged CALCOCO2WT, C-CALCOCO2, or empty vector for 24 h, followed by CVB3 infection (MOI = 10) for 7 h. Virus titer (mean ± SD, n = 3) were measured by TCID50 and western blotting was performed to confirm the expression of exogenous CALCOCO2 using an anti-Flag antibody. d Knockout (KO) efficiency of the CALCOCO2 KO HeLa cells was verified by western blotting with anti-CALCOCO2 antibody. e CALCOCO2 KO cells were transfected with empty vector, 3×FLAG-tagged CALCOCO2WT or C-CALCOCO2 for 16 h. Western blot analysis was conducted to examine the protein expression of MAVS, Flag-CALCOCO2, and ACTB. Protein levels of MAVS were quantitated by densitometric analysis, normalized to ACTB, and presented as fold changes (mean ± SD, n = 3) compared with vector control. f, g HeLa cells were co-transfected with empty vector, 3×FLAG-tagged CALCOCO2WT or C-CALCOCO2, together with either GFP-LC3 (f) or HA-Ubiquitin (g) for 16 h. Co-IP and western blotting were conducted as above. Blots for IgG heavy chain and ACTB were used as loading controls for IP and input, respectively. Results represent data from two independent experiments. h, i CALCOCO2 KO HeLa cells were transfected with empty vector, 3×FLAG-tagged CALCOCO2WT or C-CALCOCO2 for 16 h, followed by addition of poly I:C (1 μg/ml) for another 12 h. Cells were collected for RNA extraction and qRT-PCR was conducted to determine the mRNA levels of IFN-β (H, mean ± SD, n = 3). Culture supernatants were harvested for the measurement of IFN-β secretion by ELISA (I, mean ± SD, n = 3)