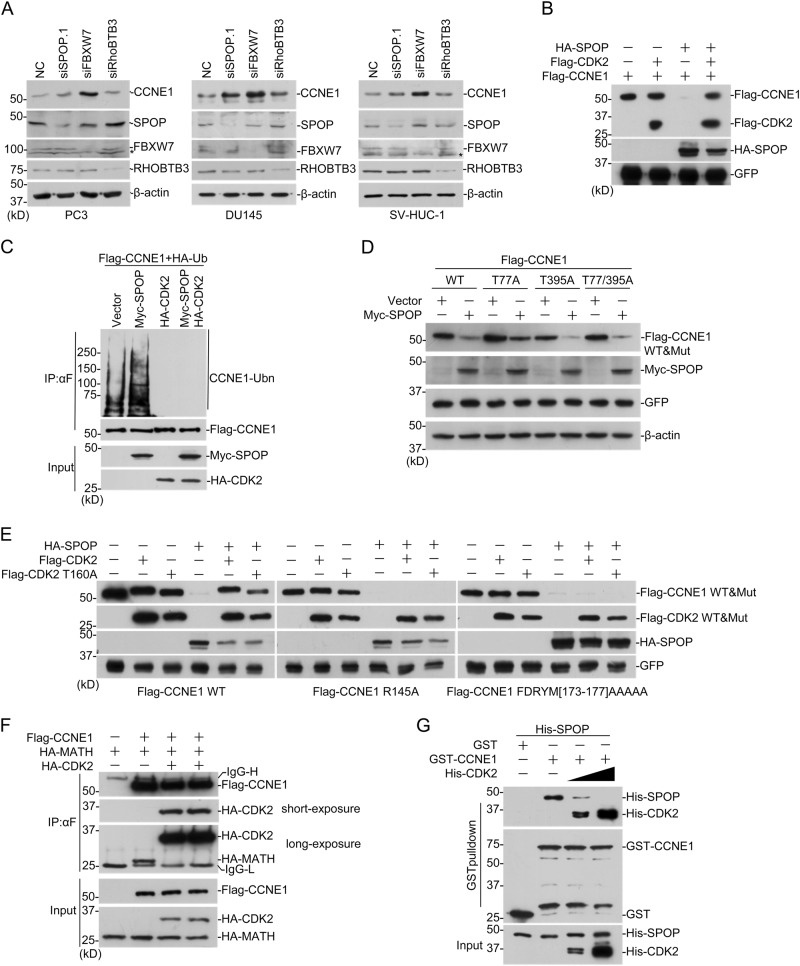
Fig. 4.
CDK2 inhibits CYCLIN E1 degradation promoted by SPOP. a PC3, DU145, SV-HUC-1 cells were transfected with SPOP/FBXW7/RhoBTB3 siRNAs. Seventy-two hours after transfection, cells were harvested for WB. b, c HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. Twenty-four hours later, cells were harvested and Flag-CCNE1 protein level (b) and ubiquitination (c) were studied. d CCNE1 plasmids were constructed with mutation of CDK2 phosphorylation sites. Then CYCLIN E1 mutants were expressed in HEK293 with or without SPOP and western blotting was performed to study CYCLIN E1 protein level. e CYCLIN E1 mutants abolishing CDK2 interaction were generated and co-expressed with CDK2 wild-type or kinase dead mutant in HEK293. Western blotting was performed to study CYCLIN E1 protein stability. f Cells were transfected with indicated plasmids and the interaction between Flag-CCNE1 and HA-SPOP (MATH domain) was studied with co-IP. g GST-pulldown was performed with bacteria-expressed proteins. The addition of His-CDK2 inhibits the interaction between GST-CCNE1 and His-SPOP