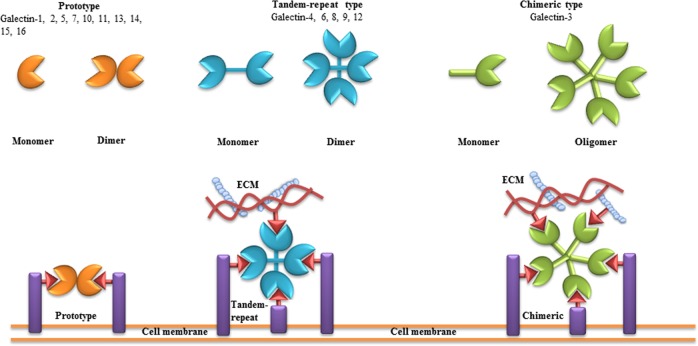
Fig. 1. Classification of galectins.
According to the number and arrangement of the carbohydrate recognition domains (CRDs), galectin family members are classified into three main types: proto, chimera, and tandem-repeat. Some galectins can self-associate into dimers or oligomers. The consensus sequence, which corresponds to the CRD, consists of ∼130 amino acids. Via their CRDs, galectins can interact with poly-N-acetyllactosamine (Gal-β(1-4)-GlcNAc, LacNAc)-based carbohydrates present in proteins, lipids, or other molecules. “One-CRD” galectins usually exist as dimers, whereas Gal-3 forms upon binding to Gal-β(1-4)-GlcNAc structures on cell surface and extracellular matrix. Tandem-repeat-type galectins comprise two homologous CRDs, separated by a short linker of up to 70 amino acids. Figure is modified from [100]