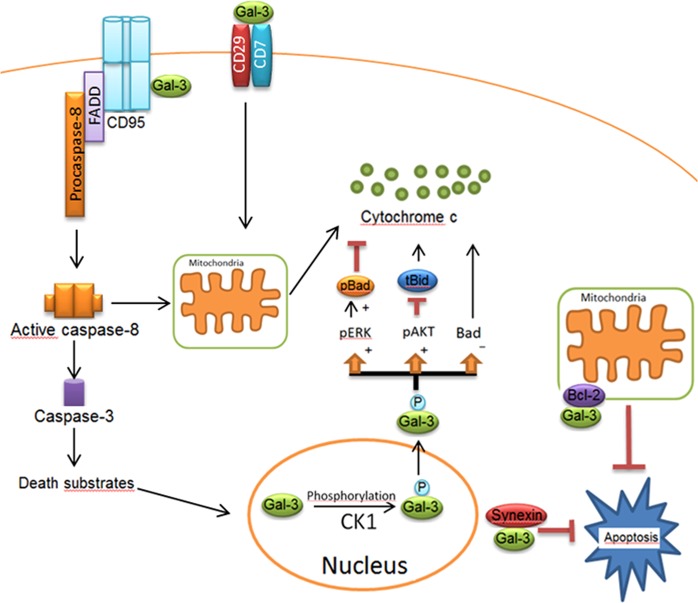
Fig. 3. Apoptotic network of Gal-3 in extrinsic and intrinsic pathways.
Gal-3 comprises a serine phosphorylation site, which is involved in its translocation into the cytosol. Following the phosphorylation of Gal-3 by Casein Kinase 1 (CK1), Gal-3 translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. The phosphorylated form of Gal-3(pGal-3) in the cytoplasm induces Bad phosphorylation via Erk pathway. pGal-3 promotes Akt activation, which blocks cleavage of Bid into tBid preventing mitochondrial outer membrane polarization. Gal-3 also attenuates cytochrome C release from the mitochondria by decreasing Bad expression. Synexin is required for Gal-3 translocation from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. In Type I cells, Gal-3 has been reported to interact with CD95, which results in high amounts of death-inducing signaling complex and active caspase-8. Extracellular Gal-3 binds to the CD29/CD7 complex, which triggers the activation of an intracellular apoptotic signaling cascade followed by cytochrome C release from mitochondria. Figure is modified from [32]