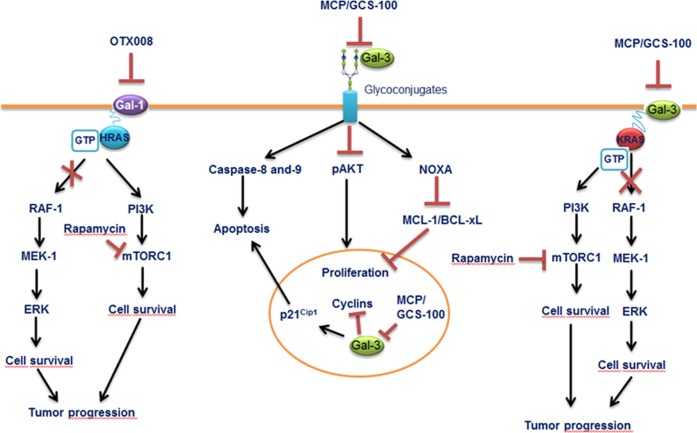
Fig. 4. Mechanisms of action of galectin inhibitors.
Inhibition of Gal-1 by OTX008 results in HRAS mistargeting to the cell membrane, leading to the blockage of mitogen-activated protein kinase mitogenic pathway, whereas rapamycin decreases mammalian target of rapamycinsurvival signaling. Combination of OTX008 and rapamycin yields more effective treatment against tumor progression. Blockage of Gal-3 with MCP/GSC-100 activates caspase-8 and -9 pathways and induces NOXA protein, leading to decrease in MCL-1 and BCL-XL. Inhibition of nuclear Gal-3 induces cell-cycle inhibitor p21Cip1 expression and blocks the expression of cyclins, leading to cell death. Inhibition of Gal-3 with MCP/GSC-100 reduces KRAS-activated tumor progression. The combined treatment using MCP/GCS-100 and rapamycin together, however, has revealed more promising results in the KRAS mutant tumor progression experimental models. Figure is modified from [101]