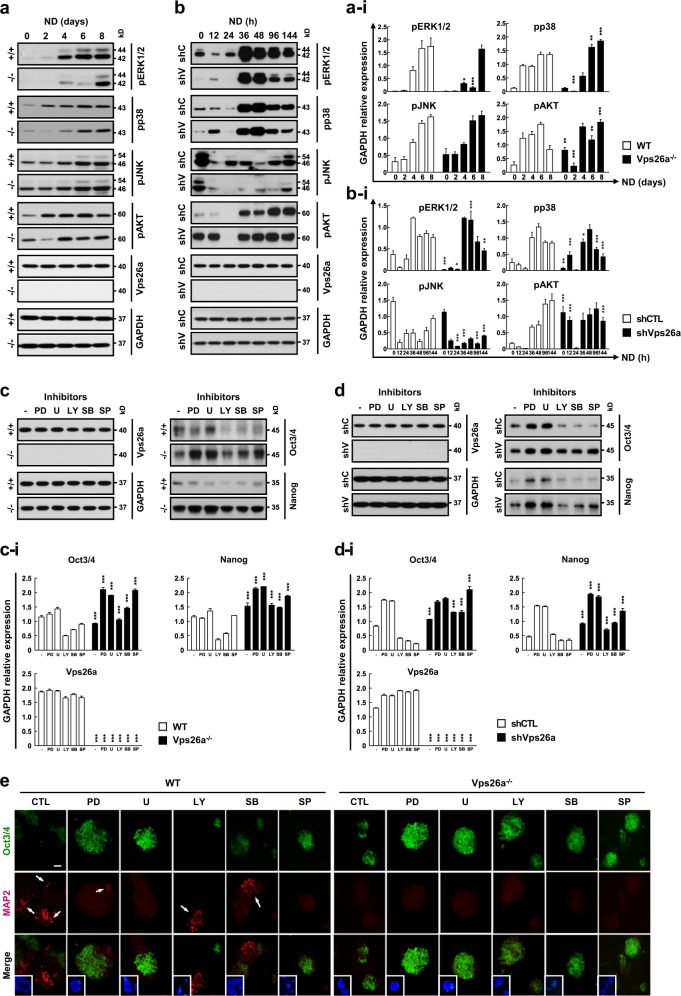
Fig. 3.
Vps26a-mediated neurogenesis depends on the ERK1/2 cascade. a, b The effects of deficiency or knockdown of Vps26a on pERK1/2, pp38 MAPK, pJNK, and pAKT levels were determined by western blotting analysis using ESCs (a) or ECCs (b), respectively, differentiated for the indicated time periods. a-i, b-i Immunoblotting quantification of (a) and (b). Western blot signals were quantified and the intensity of phosphorylated protein and the total protein normalized to the loading control GAPDH are presented (n = 3 for each group). Error bars are ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. +/+ ND 0 (a-i) and shCTL ND 0 (b-i). c, d The effect of signaling inhibitors for ERK1/2 (PD98059, PD; U0126, U), p38 MAPK (SB203580, SB), JNK (SP600125, SP), and AKT (LY294002, LY) on expression of ESC stemness markers was examined by western blot analysis of Oct3/4 and Nanog using WT (+/+) and Vps26a-/- (-/-) ESCs differentiated for 6 days (c) and shCTL (shC)- and shVps26a (shV)-ECCs differentiated for 144 h (d). c-i, d-i Immunoblotting quantification of (c) and (d). Western blot signals were quantified and the intensity of phosphorylated protein and the total protein normalized to the loading control GAPDH are presented (n = 3 for each group). Error bars are ± SD. ***P < 0.001 vs. +/+ ND 6 (c-i) and shCTL ND 6 (d-i). e Double-label immunocytochemical analysis of Oct3/4 (green) and MAP2 (red) using WT and Vps26a-/- ESCs differentiated in the presence or absence of the indicated signaling inhibitors for 6 days. DAPI staining data are shown as insets to the merged images. Scale bar, 50 μm